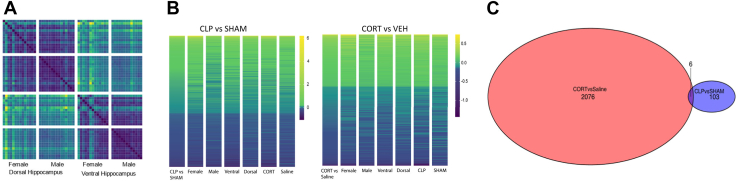
Figure 6.
(A) Poisson distance heatmap for all samples showing clear separation between samples from the dorsal and ventral hippocampus and then between samples from male and female mice, demonstrating that these factors explain most of the variation between samples. (B) Heatmap of the log-fold change top 500 genes (by p value) in the CLP vs. sham and CORT vs. VEH comparisons ordered based on log-fold change. (C) Venn diagram showing the number of significant genes (at a false discovery rate–corrected p value of .05) in CORT vs. VEH and CLP vs. sham comparisons. We saw 2082 genes that were significant in the former and 109 genes that were significant in the latter, and only 6 genes were significantly changed in both comparisons. n = 7 sham-CORT-male, n = 8 sham-CORT-female, n = 8 sham-VEH-male, n = 7 sham-VEH-female, n = 8 CLP-CORT-male, n = 6 CLP-CORT-female, n = 5 CLP-VEH-male, n = 6 CLP-VEH-female. CLP, cecal ligation and puncture; CORT, corticosterone; VEH, vehicle.