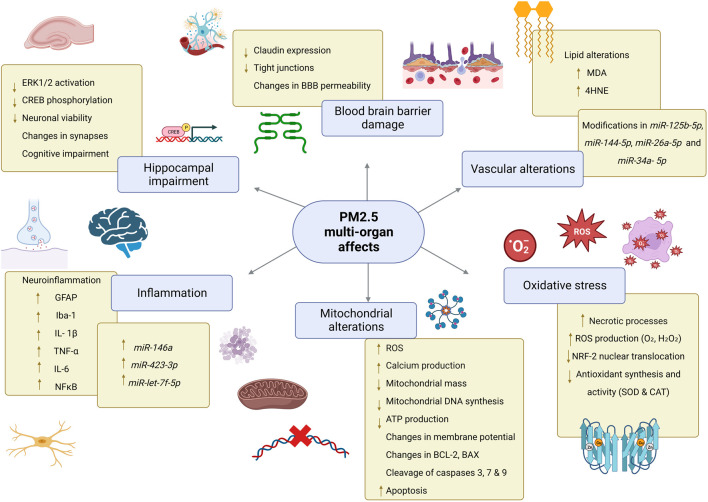
FIGURE 2.
PM2.5 multi-organ effects. Exposure to PM2.5 promotes alterations in mitochondria which in turn are associated with increased production of reactive oxygen species causing oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, and increased apoptosis. In the BBB, claudin expression and tight junction formation are reduced, impairing the integrity of this barrier. In the hippocampus PM2.5 promotes cell damage that alters neuronal communication and causes cognitive impairment. In different tissues, PM induce differential expression of miRNAs. Abbreviations: PM2.5, particulate matter 2.5; CNS, Central Nervous System; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; ATP, Adenosine triphosphate; O2・, superoxide radical; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; SOD, superoxide dismutase; CAT, catalase; MDA, Malondialdehyde; 4-HNE, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal; BBB, blood-brain barrier; ERK 1/2 Extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2; CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; Iba-1 ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule; NF-kB, nuclear factor kappa B; TNF-α tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL-1β, interleukin 1 beta; IL-6, interleukin 6; BCL-2, B cell lymphoma 2; BAX, Bcl-2 Associated X-protein.