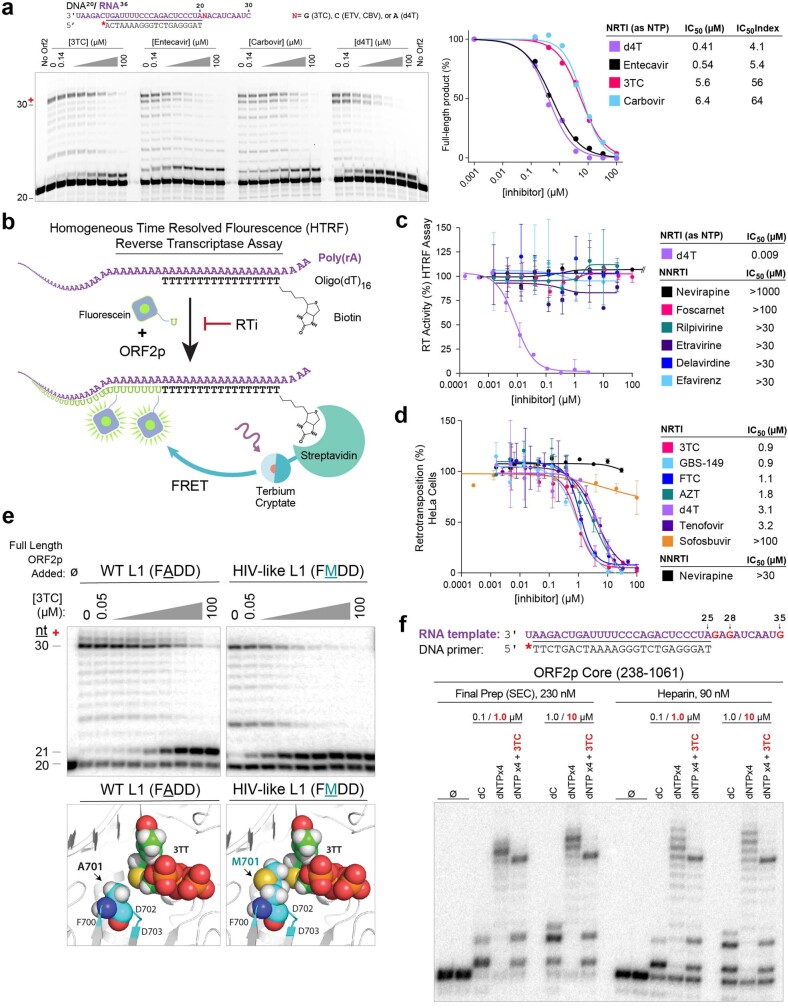
Extended Data Fig. 7. Inhibition of ORF2p core by NRTI and NNRTI reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
a, NRTIs are inhibitors of the RT activity of ORF2p core. Denaturing PAGE migration pattern (left) of RT reactions inhibited by NRTIs and their quantification (right) indicate NRTIs are potent (low µM IC50) inhibitors of ORF2p core. ORF2p core was preincubated with a template:primer containing a single site for the incorporation of a given nucleotide analogue. The primer/template sequence shown in the panel a illustrates the case of single incorporation of 3TC, with a single G for incorporation; the incoming template sequence for entecavir and carbovir has a single C, and for d4T a single A, each at position labeled “N”. Reactions were incubated for one minute at 37 °C with a 100 nM dNTP mixture and increasing concentrations of listed inhibitors. IC50 index, fold = IC50 (drug, µM) ÷ [dNTP] (natural counterpart, µM, here 0.1 µM) and reflects the fold-excess of a required NRTI over its natural counterpart to give a 50% inhibition in DNA synthesis. b, Schematic of homogenous time-resolved FRET RT (HTRF) assay. Fluorescein-labeled dNTPs (here, uracil-TP) are incorporated by ORF2p into a biotinylated primer, here shown against a poly(A) template. Detection is then achieved using FRET with a terbium cryptate labeled streptavidin, and the time-resolved technique and time-delayed emission from terbium cryptate reduces background from other fluorescent chemicals in the mix. In the presence of ORF2p RT inhibitors (RTIs), base incorporation is stopped and FRET signal is lost. For NNRTIs the indicated poly(A)-oligo(dT) template:primer is used; for NRTIs, a template:primer pair of RNA36:biotin-DNA25 is used. c, Quantification of HTRF screen shows HIV NNRTIs do not inhibit ORF2p, even at concentrations up to 1 mM for nevirapine. Upon binding of NNRTIs, such as nevirapine, the primer grip and the 94–102 segment shift which, together with movement of Y181 and Y188, open the NNRTI pocket. Accordingly, mutations of the 94–102 segment, Y181 and Y188 have all been implicated in resistance to multiple NNRTIs65–72; n = 3 independent wells representative of two independent experiments. d, Inhibition assay in HeLa cells stably expressing a dual luciferase L1 retrotransposition reporter73, normalized to cell viability using Cell Titer Glow reagent; n = 3 biologically independent wells representative of two experiments. e, 3TC analog in the context of the native FADD active site loop (left) and 3TC analog in the context of the mutant FMDD active site loop (right). Note the lack of van der Waals contacts between the Ala 701 side chain and the oxathiolane ring, including the sulfur atom, in the nucleotide in the native active site, contrasted with the favorable contact between the Met 701 and the oxathiolane ring in the nucleotide. Similar effects were shown previously in the YADD mutant of HIV (WT YMDD)74. f, Full length ORF2p and ORF2p core are compared in single nucleotide incorporation and inhibition experiments with the indicated nucleoside triphosphates and 3TC triphosphate; ‘dNTPx4’ is a mix of all four standard dNTPs. Full length ORF2p (purity insufficient to accurately determine concentration) produces similar reaction products and shows similar activity and inhibition to both partially-purified (Heparin) and fully-purified (after SEC) ORF2p core. This assay qualitatively reveals both incorporation and tolerance for some misincorporations of the polymerase. For example, in the ‘dC’ lane, containing only dCTP, the 26 nt band represents one C-G incorporation, and the 28 nt band is from subsequent C-A misincorporation followed by a C-G incorporation. Adding 3TC chain-terminates products and the strong bands at at 26, 28, and 35 nt highlight the G-base positions in the template.