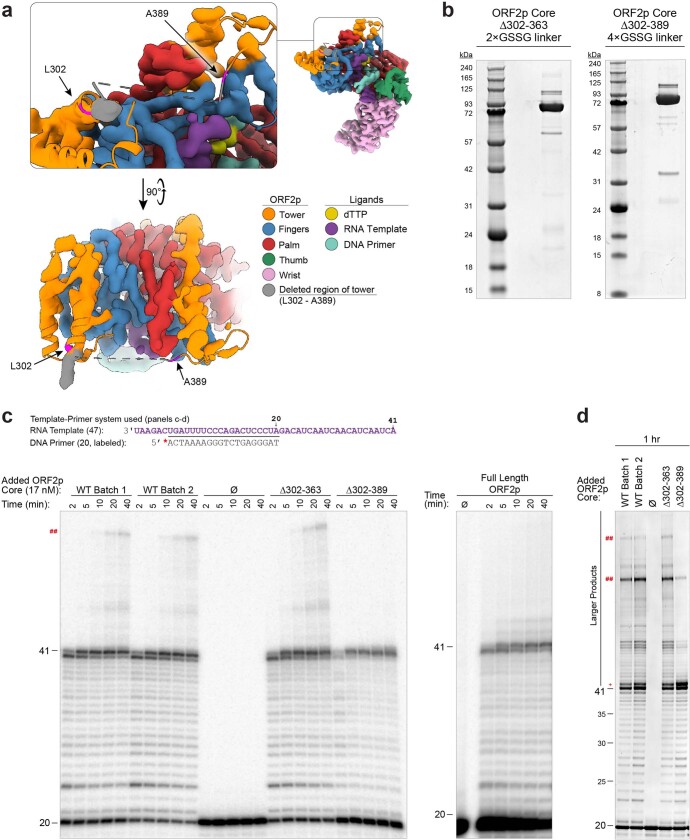
Extended Data Fig. 3. Design and characterization of the ORF2p tower domain deletions reveal it is not required for RT.
To test the role of the tower and tower lock in reverse transcription, ORF2p core constructs where the tower was deleted at two different points were designed. a, The maximal tower deletion construct (∆302–389) represents removal of the unresolved tower and the tower lock residues from both the EM and crystal structures as evidenced by mapping the deletion back onto the EM structure of ORF2. The shorter tower deletion ∆302–363 deletes the tower but preserves the lock. b, SDS-PAGE analysis of monodisperse ORF2p core tower deletion constructs show relatively pure enzyme ( > 90%). c, Comparison of wildtype ORF2p core and full length versus ∆302–363 and ∆302–389 (cropped in Fig. 2d) shows similar RT activity between all constructs with little difference in efficiency of formation of 41 nt full length products over time; full length and ∆302–389 are slightly less specifically active, which may be due to batch effects, contaminants, or concentration estimation errors; 17 nM of purified ORF2p core constructs was reacted with 0.1 μM dNTP mixture and samples taken over time. Asterisk (*) 32P-labeled 5’-end of the primer. d, Comparison of wildtype and tower deletion ORF2p core constructs under longer reaction conditions with higher concentrations of enzyme and nucleotide shows all constructs form full length, NTA ( + and above), and template jumping/switching products (##), although the yield of these larger products correlates with specific activity; it appears that here and in panel (c), deletion of both the tower and lock (∆302–389) may selectively negatively impact template jumping/switching activity, although this may be attributable to either lock or the way in which it was deleted, and further investigation is warranted. These reactions are 1 h with 3-fold more enzyme (50 nM) and 10-fold more dNTPs (1 μM). Scanned gel images are cropped and corrected for distortion artifacts with contrast uniformly increased to facilitate the visualization of minor products.