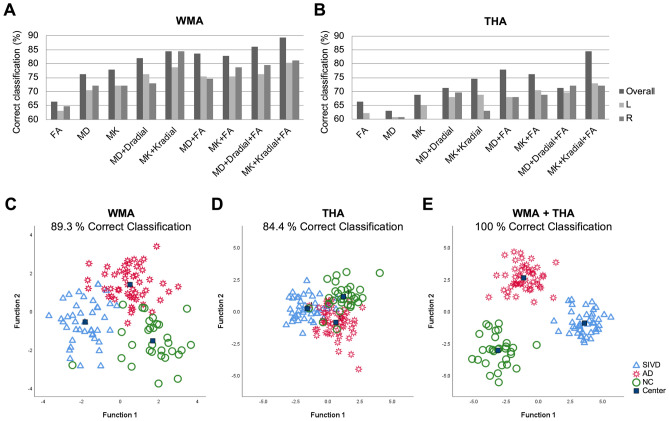
Figure 1.
Discriminant analysis determined by kurtosis and diffusion metric selection. (A, B) Comparisons of variable metrics (e.g., MK, MD, and FA) by two measures (i.e., WMA and THA) shows that integration of triple metrics (MK + Kradial + FA) achieves the best discriminant analysis of aging spectrum including SIVD, AD, and NC (89.3% and 84.4% correct classification in the WMA and THA, respectively. In the WMA, the correct classification rate by single/double/triple metrics is 66.4–77.9/82.0–84.4/86.1–89.3%, with the averaged correct classification rate of 73.5/83.2/87.7%, respectively. In the THA, the correct classification rate by single/double/triple metrics is 63.1–68.9/71.3–77.9/71.3–84.4%, with the averaged correct classification rate of 66.1/75.0/77.9%, respectively. The correct classification rates of utilizing single/double/triple metrics were derived by entering the selected diffusion metrics (e.g. MK, MD, FA, …etc.) from white matter atlas or thalamic atlas in to discriminant analysis. Data from different hemispheres were regarded as different inputs. Taking a triple-metric (MK + MD + FA) as an example, such triple-metric in bilateral WMA (total 16 regions) will give 48 values in each individual, and these 48 values are entered into discriminant analysis. The optimized kurtosis metrics (i.e., MK + Kradial + FA) is further examined by deciphering primary regions of interest by hemispheres, showing 80.7 and 72.3% average correct classification in the WMA and THA, respectively. (C–E) Discriminant analysis results from the optimized kurtosis metrics are plotted, showing that 89.3% correct classification in the WMA, 84.4% correct classification in the THA, and 100.0% correct classification in WMA + THA. R/L = Right/Left hemisphere. FA = fractional anisotropy; MD = mean diffusivity; MK = mean kurtosis; Dradial = radial diffusivity; Kradial = radial kurtosis. WMA = White matter atlas. THA = Segregated thalamus analysis. SIVD = Subcortical ischemic vascular disease. AD = Alzheimer's disease. NC = normal cognition.