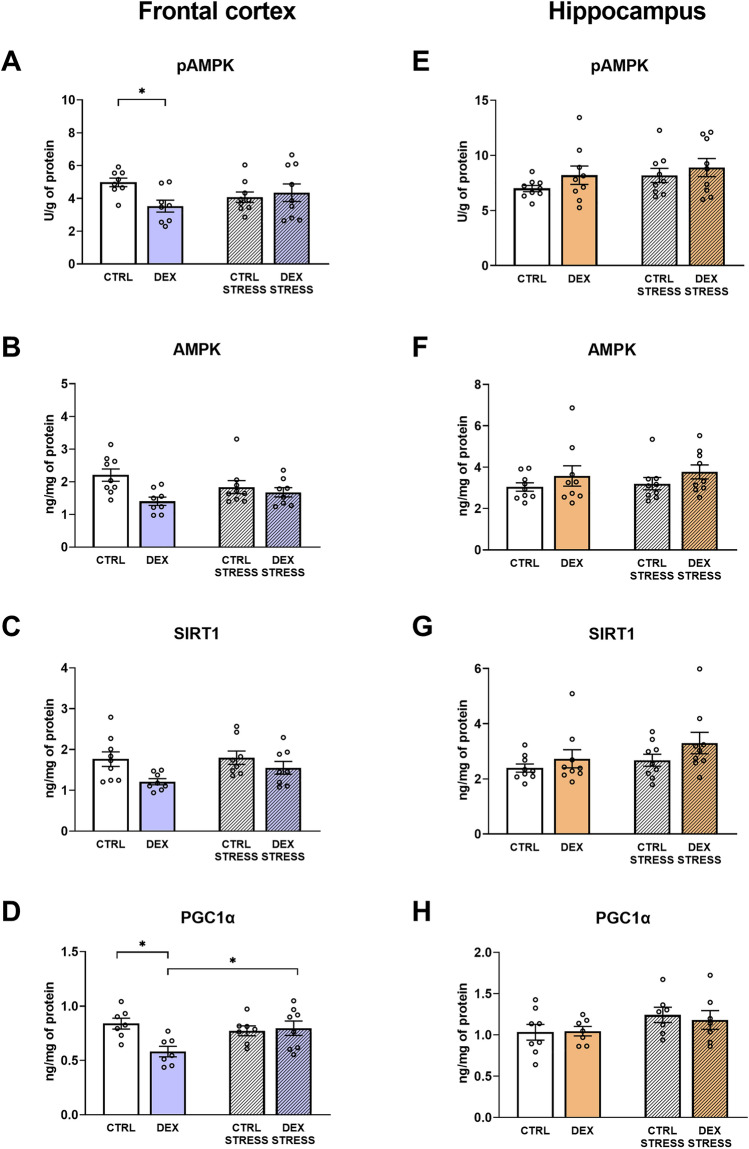
Fig. 4.
Effect of prenatal dexamethasone treatment and acute stress in adulthood on the level of phospho-AMPK (A), AMPK (B), deacetylase SIRT1 (C), and PGC1α receptor (D) in the frontal cortex and hippocampus (E, F, G, and H, respectively) of male rats; the level of proteins was assessed with ELISAs and expressed in U/g of protein (pAMPK) or ng/mg of protein (AMPK, SIRT1, and PGC1α); bar graphs represent the mean ± SEM. Statistics: two-way ANOVA, followed by the Duncan post hoc test; n = 7–9; *p < 0.05; in the case of AMPK and SIRT1 levels in the frontal cortex, DEX main effect was significant at F1,30 = 7.800; p = 0.009 and F1,29 = 7.051; p = 0.013, respectively