Fig. 9.
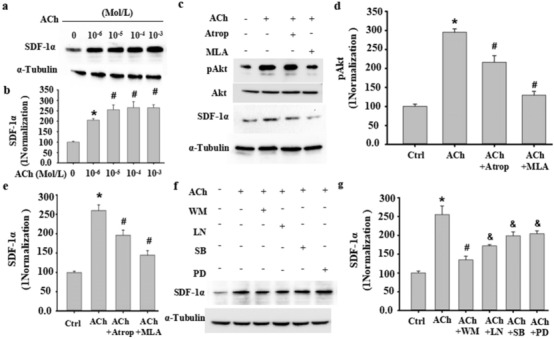
ACh induced SDF-1α in VSMCs through the m/n-AChR-Akt signaling pathway. a, b ACh dose-dependently induced SDF-1α expression in VSMCs, as detected by Western blot (a). (b) Semiquantitative analysis of SDF-1α expression in VSMCs. *P < 0.05 vs. 0 Mol/L ACh; #P < 0.05 vs. 10−6 Mol/L ACh (n = 3). c–e The increased SDF-1α and phosphorylation of Akt following ACh stimulation in VSMCs was abolished by the mACh-R inhibitor atropine (Atrop) or the nACh-R inhibitor mecamylamine, as determined by Western blot (c). d–e Semiquantitative analysis of SDF-1α expression in VSMCs. *P < 0.05 vs. 0 Mol/L ACh; # P < 0.05 vs. 10−5 Mol/L ACh (n = 3). f–g Signaling pathways mediating ACh-induced SDF-1α expression were assessed by pathway-specific inhibitors as indicated. Western blotting was used to detect ACh-induced SDF-1α expression in VSMCs following treatment with wortmannin (WM, 50 nM), LN (15 nM), SB203580 (SB, 30 µM), and PD98059 (PD, 50 µM). α-Tubulin served as an internal control. g Semiquantitative analysis of SDF-1α in Fig. 7f as indicated. At least three independent experiments were carried out. *P < 0.05 vs. 0 ACh (Ctrl); # P < 0.05 vs. 10−5 Mol/L ACh; # P < 0.05 vs. ACh + WM (n = 3)
