Figure 3. Similarity of classifiers and intensifiers across emotions.
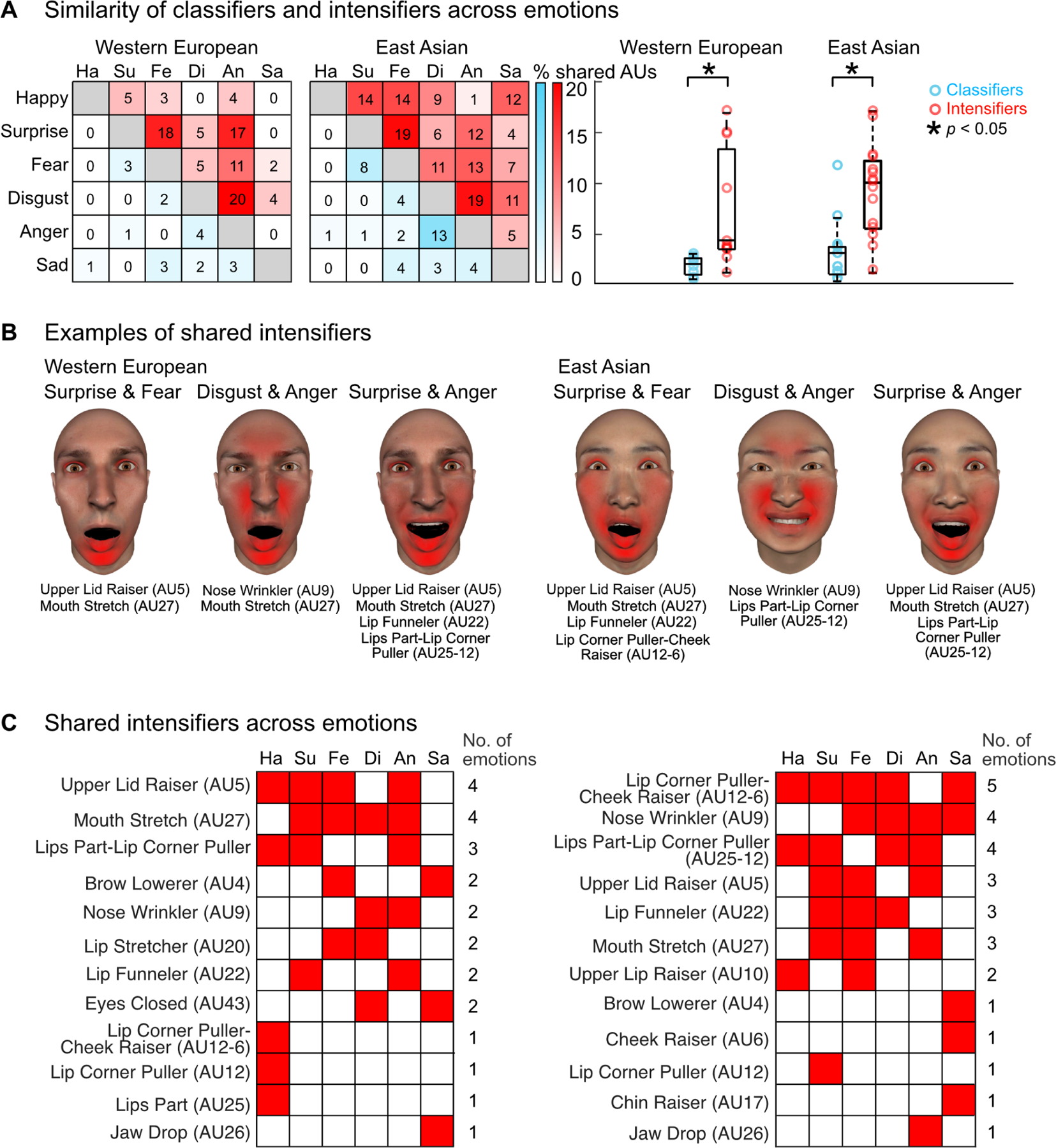
(A) For each culture, the color-coded matrix shows the percentage of emotion classifiers (blue) and intensifiers (red) that are shared across each emotion pair. Higher color saturation indicates more similarity; exact percentages are shown in each square. Color-coded circles and boxplots to the right show the data aggregated across emotion pairs; individual circle represents each emotion pair as shown in the matrix. Asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference. Results show that emotion intensifiers are significantly more similar across emotions than classifiers are (p < 0.05, two-sample t-test, see Signal distinctiveness of classifier and intensifier facial movements across emotions—STAR Methods).
(B) Examples of shared intensifiers. For each culture, face maps show examples of intensifier AUs (labels below) that are shared across emotion pairs. For example, for East Asian receivers, the wide-open eyes (Upper Lid Raiser—AU5), gaping mouth (Mouth Stretch—AU27) and lip pulling (Lips Part-Lip Corner Puller—AU25-12) intensify both ‘surprise’ and ‘anger’.
(C) Shared intensifiers across emotions. For each culture, red squares in the matrix show the emotion(s) that each AU intensifies. The total number of emotions is shown on the right. Intensifiers are ranked from the highest to lowest number of emotions. For example, for Western receivers, the wide opened eyes (Upper Lid Raiser—AU5) and gaping mouth (Mouth Stretch—AU27) intensify 4 out of 6 emotions. For East Asian receivers, lip pulling with cheek raising (Lip Corner Puller-Cheek raiser—AU12-6), nose wrinkling (Nose Wrinkler—AU9) and lip pulling with open mouth (Lips Part-Lip Corner Puller—AU12-25) each intensifies at least 4 emotions.
