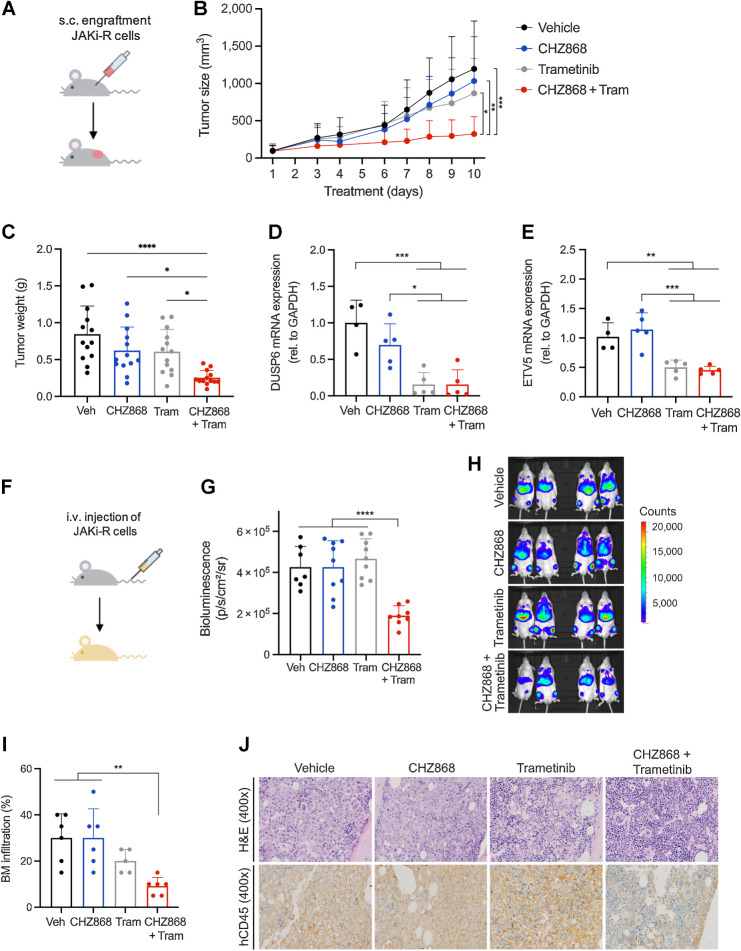
Figure 6.
Targeting MAPK pathway abrogates acquired resistance to type II JAK2 inhibition in vivo. A, Schema of in vivo model with subcutaneous engraftment. JAK2 inhibitor resistant SET2 cells (JAK2i-R) were injected into the flank of NSG mice. Animals were treated orally with type II JAK2 inhibitor CHZ868 15 mg/kg every day, MAPK inhibitor trametinib (tram) 0.3 mg/kg every day, combined CHZ868 15 mg/kg every day/MAPK inhibitor trametinib 0.3 mg/kg every day, or vehicle control. Treatment was initiated at 100 mm3 tumor size and continued until maximal tumor size was reached in vehicle-treated mice. B, Tumor size over time showed tumor growth in vehicle-treated mice similarly to CHZ868-treated mice. Combined JAK2/MAPK inhibition effectively reduced tumor size (n = 13/group). C, Analysis of tumor weight at end of treatment confirmed significant reduction of tumor growth in vivo by combined JAK2/MAPK inhibition with CHZ868 15 mg/kg every day/MAPK inhibitor trametinib 0.3 mg/kg every day (n = 13/group). D, Expression of MAPK pathway target DUSP6 was significantly reduced by combined JAK2/MAPK inhibition with CHZ868 15 mg/kg every day/MAPK inhibitor trametinib 0.3 mg/kg every day (n = 4–5/group). E, Expression of MAPK pathway target ETV5 was significantly reduced by combined JAK2/MAPK inhibition with CHZ868 15 mg/kg every day/MAPK inhibitor trametinib 0.3 mg/kg every day (n = 4–5/group). F, Schema of in vivo model with intravenous engraftment. JAK2 inhibitor resistant SET2 cells (JAK2i-R) stably expressing luciferase were injected intravenously into NSG mice and engraftment documented by bioluminescent imaging. Animals were treated orally with type II JAK2 inhibitor CHZ868 15 mg/kg every day, MAPK inhibitor trametinib 0.3 mg/kg every day, combined CHZ868 15 mg/kg every day/MAPK inhibitor trametinib 0.3 mg/kg every day, or vehicle control. G, Bioluminescent signal was significantly reduced in mice treated with combined CHZ868/trametinib at 7 days of treatment (n = 7–9/group). H, Representative bioluminescence images are shown. I, BM infiltration of JAK2i-R cells was determined as human CD45 positivity by IHC on BM sections. A significant reduction of BM infiltration was observed with combined CHZ868 15 mg/kg every day/MAPK inhibitor trametinib 0.3 mg/kg every day (n = 5–6/group). J, Representative images of BM sections stained with H&E (top) and IHC for hCD45 (lower panel) showed reduced infiltration with combined CHZ868 15 mg/kg every day/MAPK inhibitor trametinib 0.3 mg/kg every day. Original magnification x400. Data are presented as mean ± SD and analyzed by one-way ANOVA. ns, not significant; *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; ****, P ≤ 0.0001.