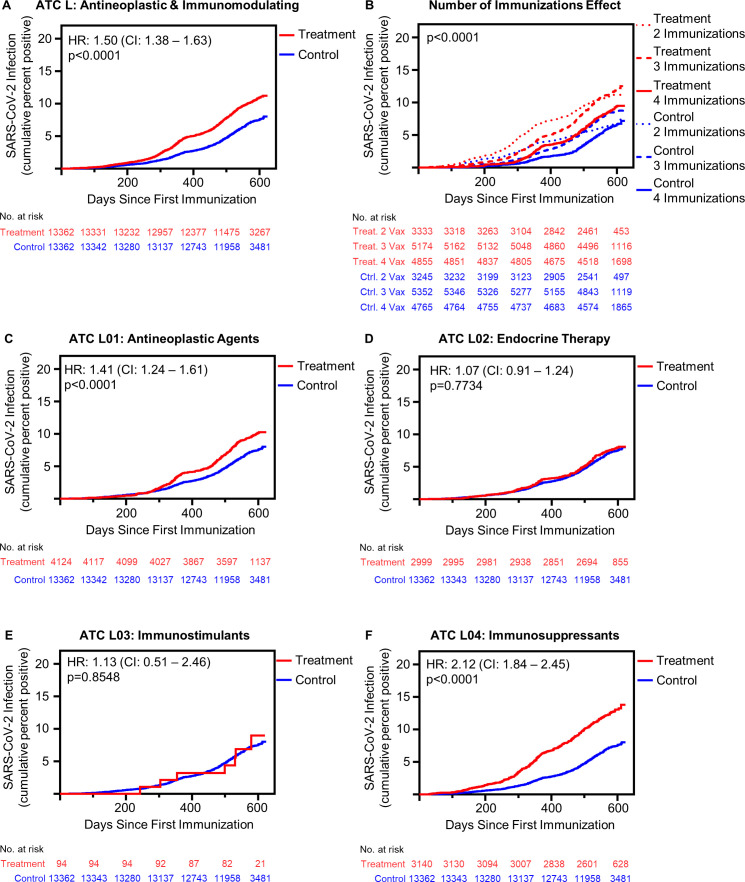
Figure 1.
Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents associated with increased risk of postimmunization SARS-CoV-2 infection in a class dependent manner. (A) Cumulative incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection following initial immunization in all patients receiving antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents (treatment, n=13 362) compared with matched control patients (n=13 362) (p<0.001 by log-rank). (B) Effect of multiple immunizations on SARS-CoV-2 infection incidence postimmunization (treatment: 2 immunizations n=3333, 3 immunizations n=5174, 4 immunizations n=4855; control: 2 immunizations n=3245, 3 immunizations n=5352, 4 immunizations n=4765) (p<0.001 by log-rank square). (C) SARS-CoV-2 infection cumulative incidence following initial immunization in all patients receiving L01: antineoplastic agents, patients receiving multiple medications excluded from analysis (L01 antineoplastic agent receiving patients n=4124) (p<0.0001 by log-rank). (D) SARS-CoV-2 infection cumulative incidence following initial immunization in all patients receiving L02: endocrine therapy, patients receiving multiple medications excluded from analysis (L02 endocrine therapy receiving patients n=2999) (p=0.7734 by log-rank). (E) SARS-CoV-2 infection cumulative incidence following initial immunization in all patients receiving L03: immunostimulants, patients receiving multiple medications excluded from analysis (L03 immunostimulant receiving patients n=94) (p=0.8548 by log-rank). (F) SARS-CoV-2 infection cumulative incidence following initial immunization in all patients L04: immunosuppressants, patients receiving multiple medications excluded from analysis (L04 immunosuppressant receiving patients n=3140) (p<0.0001 by log-rank). ATC, Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical.