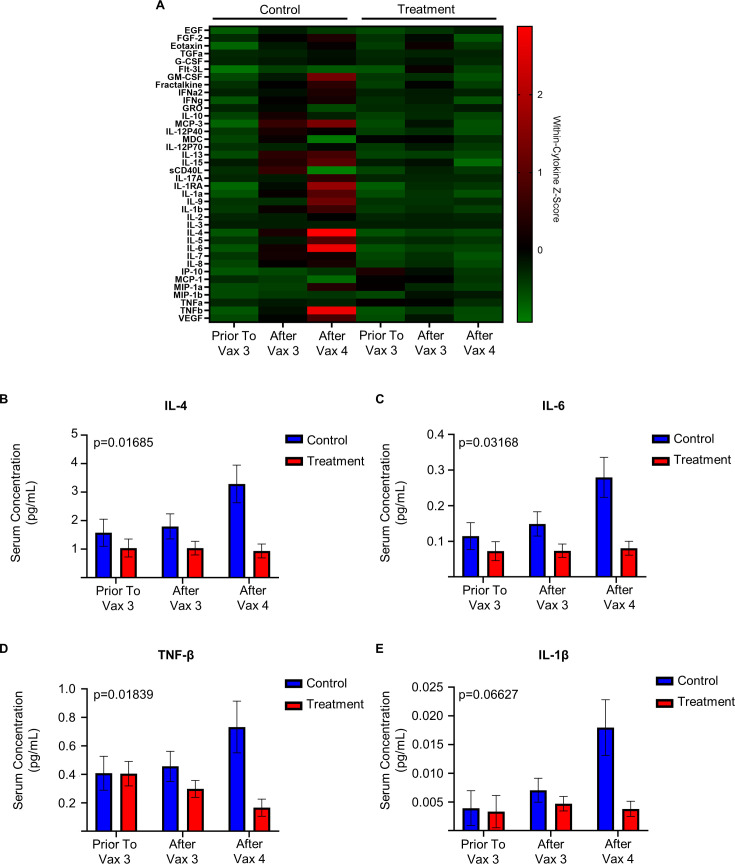
Figure 4.
Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents are associated with decreased serum cytokine concentration after immunization in patients receiving antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents. (A) Serum cytokine concentration of patients receiving antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents (treatment) and participants not receiving these medications (control) relative to third (Vax 3) and fourth (Vax 4) COVID-19 immunization (Treatment prior to Vax 3 n=10, after Vax 3 n=70, after Vax 4 n=68; control prior to Vax 3 n=9, after Vax 3 n=28, after Vax 4 n=6). Within cytokine Z-score demonstrated from normalized Luminex Immunoassay. (B) Serum concentration (pg/mL, mean estimated by Restricted Maximum Likelihood (REML)-mixed effect model, error bars represent SEM) of IL-4 of treatment and control participants. (p=0.01685 by ANOVA main interaction effect). (C) Serum concentration (pg/mL, estimated by REML-mixed effect model) of IL-6 of treatment and control participants. (p=0.03168 by ANOVA main interaction effect). (D) Serum concentration (pg/mL, estimated by REML-mixed effect model) of TNF-β of treatment and control participants (p=0.01839 by ANOVA main interaction effect). (E) Serum concentration (pg/mL, estimated by REML-mixed effect model) of IL-1β of treatment and control participants. (p=0.06627 by ANOVA main interaction effect, p=0.0245 ANOVA treatment effect). ANOVA, analysis of variance.