Fig. 4.
The activity of c-Myc is controlled by SNIP1.
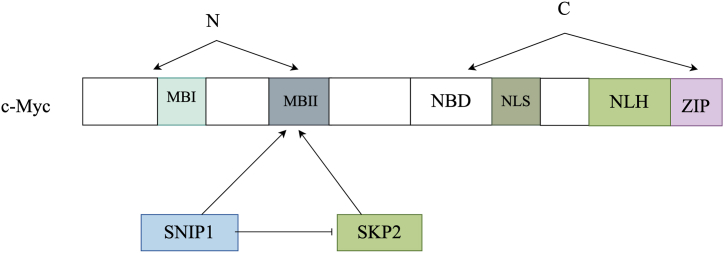
c-Myc's N-terminal region contains the Myc boxes (MBI and MBII), which are crucial for its transcriptional activity. Conversely, the C-terminal contains a nonspecific DNA-binding domain (NDB), a nuclear localization signal (NLS), and a helix-loop-helix (HLH) motif. The FHA-containing C terminus of SNIP1 interacts with the N-terminal region of c-Myc, thereby enhancing its transcriptional activity. S phase kinase-associated protein 2 (Skp2) facilitates c-Myc ubiquitylation by binding to the MBII domain, regulating the degradation of c-Myc through the proteasome pathway. Both SNIP1 and Skp2 compete for binding to c-Myc.