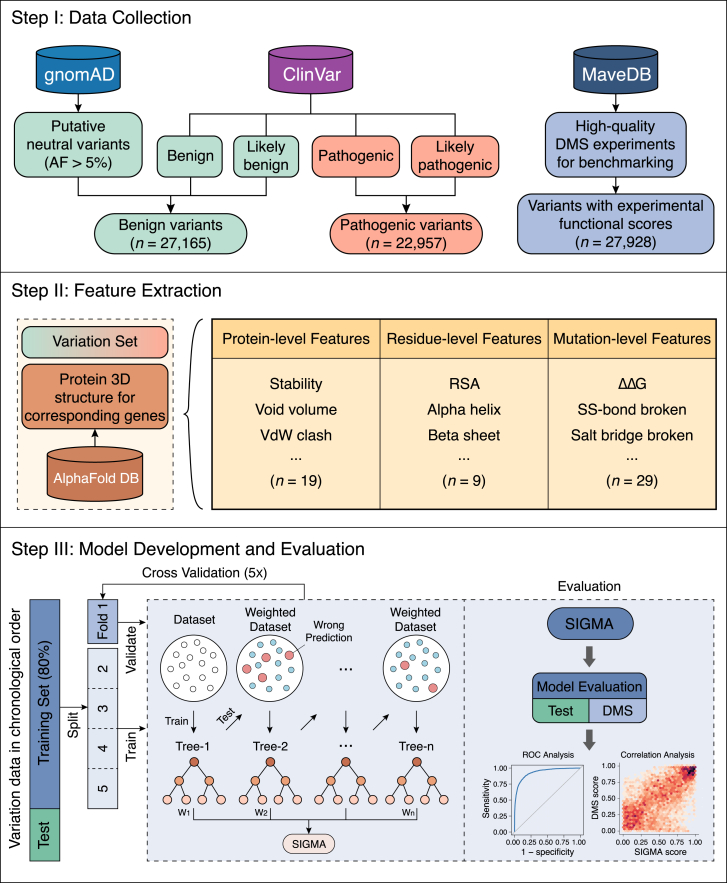
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the study design
Step 1: data collection of variant datasets. A total of 27,165 benign and 22,957 pathogenic missense variants were retrieved from gnomAD and ClinVar databases as the “gold standard.” In addition, 27,928 variants in six proteins systematically characterized by DMS experiments were included to provide an independent measurement for assessing predictors. Step 2: extraction of structure-informed features. For each variant, 57 features were extracted based on protein 3D structure predictions. Step 3: development and evaluation of SIGMA. The gold standard dataset was sorted in chronological order and divided with 80% used for training and 20% for testing (see STAR Methods). Using the GBM algorithm, we developed SIGMA to predict the variant pathogenicity. ROC analysis and correlation analysis were used to evaluate the performance of SIGMA on the test dataset and the DMS dataset, respectively. DMS, deep mutational scanning; 3D, three-dimensional; SIGMA, structure-informed genetic missense mutation assessor; GBM, gradient boosting machine; ROC, receiver operating characteristic; RSA, relative solvent accessibility; ΔΔG, the unfolding free energy difference between the wild-type and mutant protein; SS-bond: disulfide bond.