Figure 1. Body weight and survival curves of B6-Sumf1A277V/A277V and B6-Sumf1S153P/S153P mutant strains.
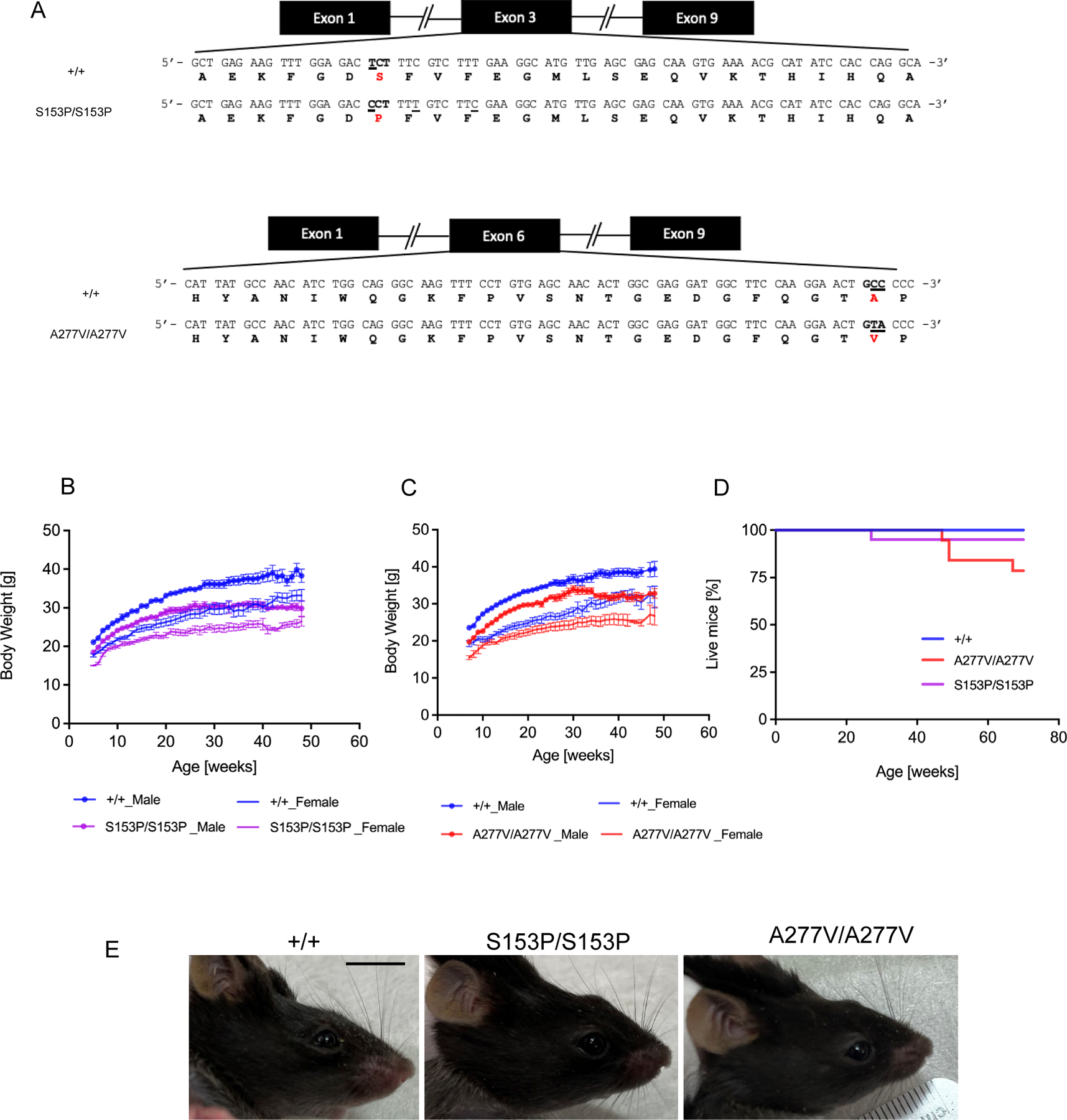
(A) Amino acid substitutions in Sumf1 exon 3 (p.Ser153Pro) (upper panel) corresponding to the human SUMF1 pathogenic variant p.Ser155Pro and exon 6 (p.Ala277Val) (lower panel) corresponding to human SUMF1 pathogenic variant p.Ala279Val. Nucleotide changes are underlined. (B) Body weight of Sumf1S153P/S153P (S153P/S153P) and (C) Sumf1A277V/A277V (A227V/A227V). (D) and Kaplan-Meyer survival curves of both mouse lines compared to wild type Sumf1+/+ (+/+) mice. n=10 for each sex and genotype. (E) Sumf1S153P/S153P (S153P/S153P) and Sumf1A277V/A277V (A227V/A227V) mice exhibited a craniofacial defect compared to wild type Sumf1+/+ (+/+) mice. Scale bar = 1 cm. Data are shown as means ± SEM.
