Figure 8.
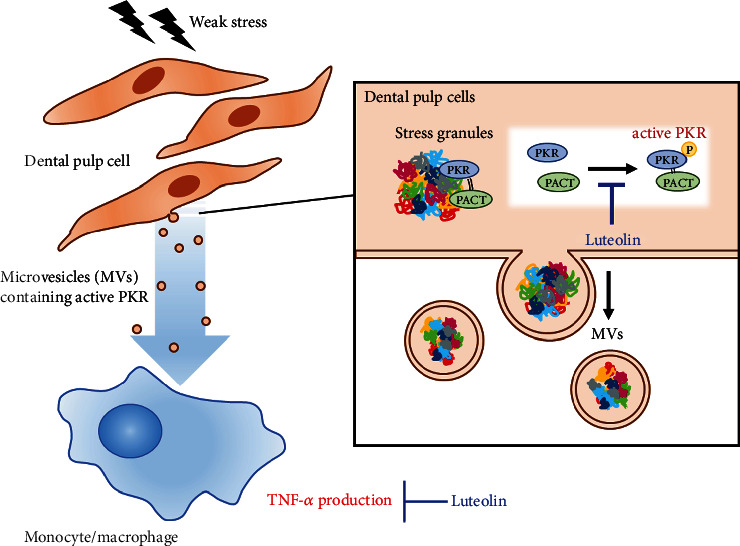
Luteolin induces its therapeutic effect on pulpitis of DP-1-derived MVs by inhibiting the activation of PKR. In dental pulp cells, weak stress signals induce protein kinase R (PKR) phosphorylation, resulting in the release of active PKR-containing microvesicles (MVs), which function as an extremely powerful TNF-α inducer in monocytes and macrophages (left). PKR-activating protein (PACT), an endogenous PKR activator, enhances PKR phosphorylation in stress granule complexes. Luteolin antagonizes the interaction between PKR and PACT to inhibit PKR activation, which could be a potential strategy for suppressing the onset of pulpitis (right).
