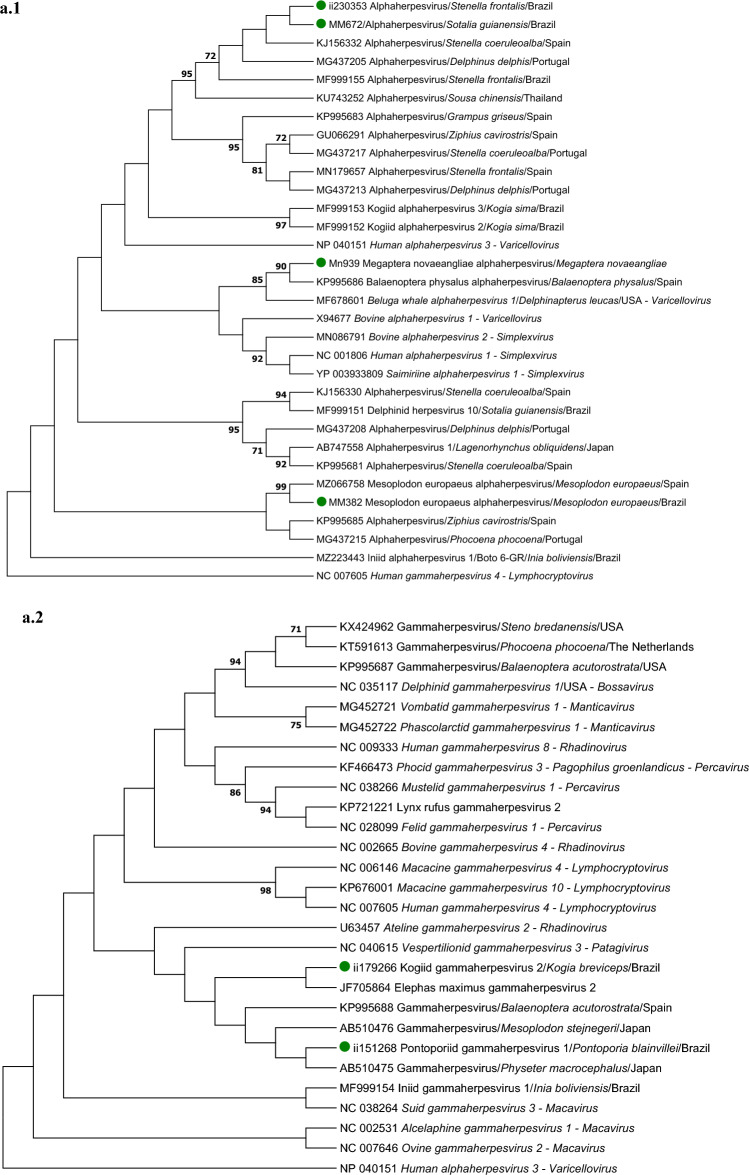
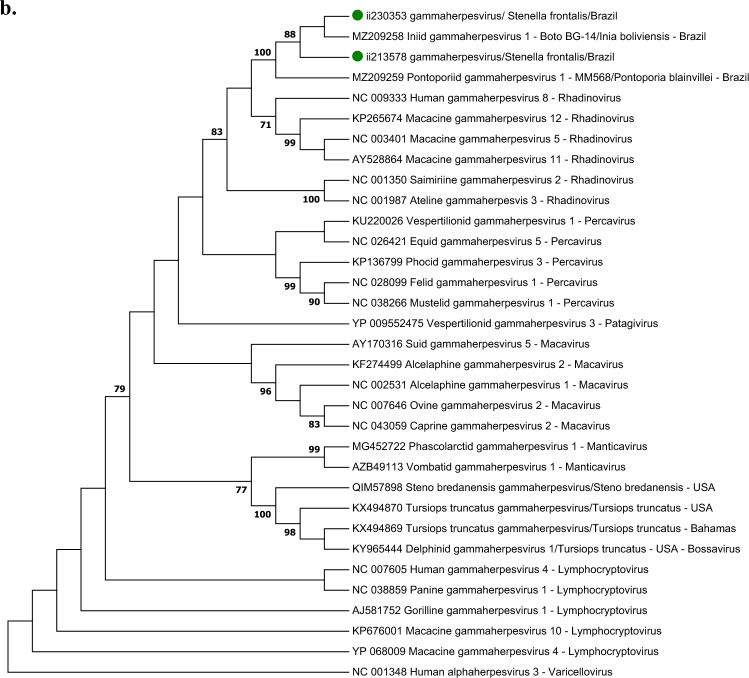
Figure 1.
(A) Maximum likelihood phylogram of the herpesvirus DNA polymerase (DPOL) deduced amino acid sequences: (i) obtained in this study (green dots), (ii) the closest to these sequences from GenBank, (iii) alpha- and gammaherpesvirus sequences retrieved from other cetacean species, (iv) sequences of alpha- and gammaherpesvirus species recognized by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV); the DPOL alphaherpesvirus phylogram (a.1) was based on the Jones Taylor Thornton gamma distributed with invariant sites model, while the gammaherpesvirus phylogram (a.2) was based on Le Gascuel gamma distributed with invariant sites model. (B) Maximum likelihood phylogram based on the Le Gascuel substation model with gamma distribution of the herpesvirus glycoprotein B deduced amino acid sequences (i) obtained in this study (green dots), (ii) the closest sequences to these sequences from GenBank, (iii) gammaherpesvirus sequences retrieved in other cetacean species, and (iv) gammaherpesvirus species recognized by the ICTV. Human gammaherpesvirus 4, Human alphaherpesvirus 3 and Human alphaherpesvirus 3 were selected as outgroup for alphaherpesvirus DPOL, gammherpesvirus DPOL and glycoprotein B phylograms. The reliability of the phylograms was tested via 1.000 bootstrap, and those bootstrap values lower than 70 were omitted.