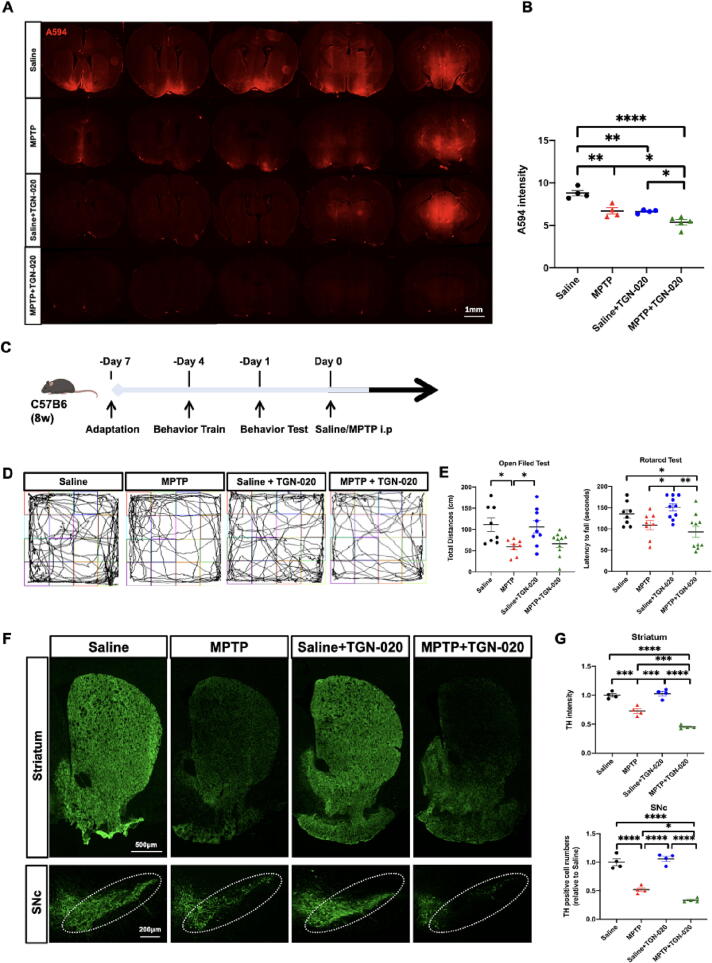
Fig. 3.
AQP4 inhibition disrupts glymphatic drainage and aggravates PD pathology. A-B: Quantification of the mean intensity of A594 penetration into the whole brain parenchyma in both Saline and MPTP groups after inhibition of TGN-020 (n = 4–5 per group). C: Time schedules of the behavioral experiment and representative images of the open-field test. D-E: Quantification of the total traveled distance in the open-field test (n = 8–10 per group) and the latency to falling in the rotarod test (n = 8–10 per group) after TGN-020 treatment. F: Representative immunofluorescence staining of TH-positive neurons in the striatum and SN compacta (SNc) of the mouse brain. White dotted circles indicate the SNc regions. G: Quantification of the TH intensity in the striatum and TH-positive cell numbers in SNc after TGN-020 treatment (n = 4 per group). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. One-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test were performed. Scale bars are indicated.