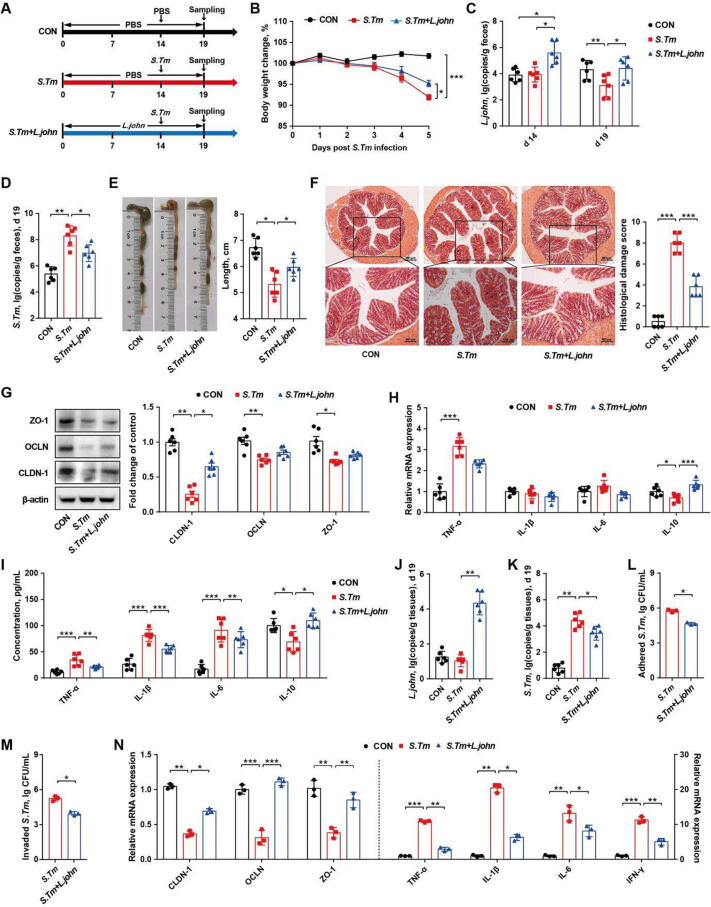
Fig. 7.
L. johnsonii alleviates Salmonella infection by inhibiting pathogenic adhesion and invasion of intestinal epithelial cells. (A) Experimental scheme. (B) Body weight changes. (C) Fecal titers of Salmonella on d 14. (D) Fecal titers of Salmonella on d 19. The colon length (E), histological score (F), tight junction protein expression levels (G), and cytokine mRNA expression levels (H) in the colon as well as plasma immune cytokine levels (I) were indicated. Copies of L. johnsonii (J) and Salmonella (K) on the colonic mucosa on d 19. Adhesive (L) and invasive (M) abilities of Salmonella to the epithelial cells. (N) Relative mRNA expression of tight junction proteins and immune cytokines in HT-29 cells. CON, mice treated with PBS; S. Tm, Salmonella-infected mice; L. john, mice received both L. johnsonii and Salmonella. OCLN, occludin; CLDN-1, claudin-1; ZO-1, zonula occluden-1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-10, interleukin-10. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001.