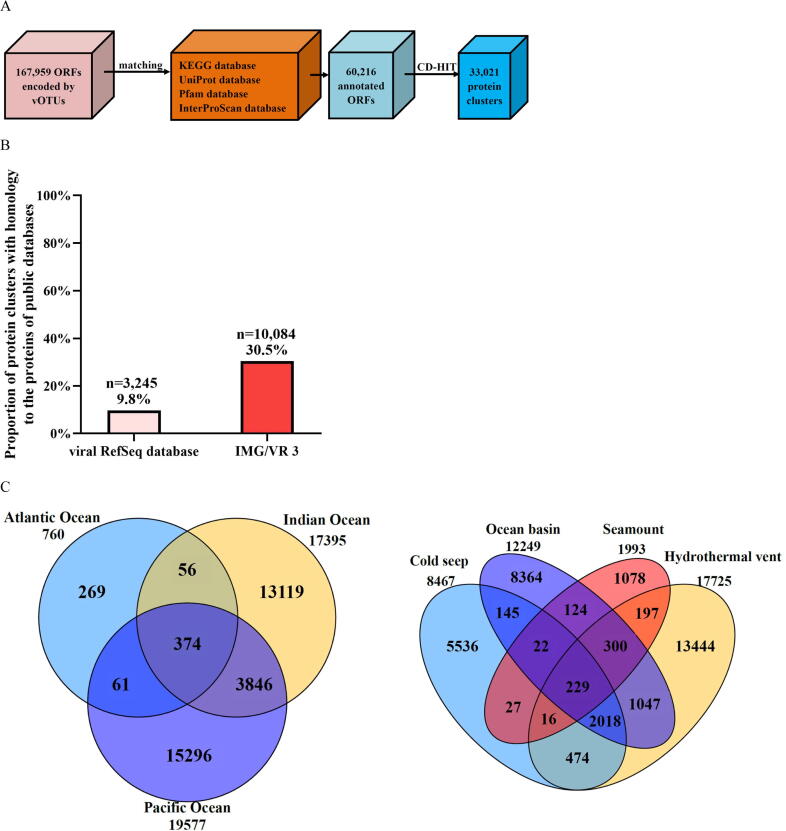
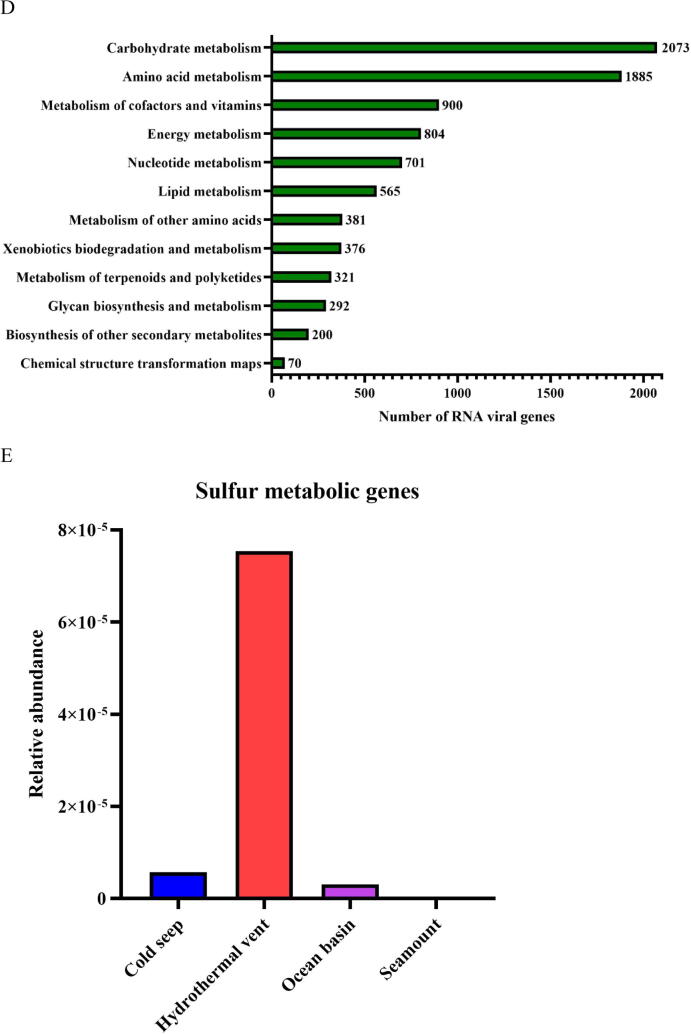
Fig. 5.
Influence of viral genes on the community differentiation of deep-sea RNA viruses. (A) Diagram showing the identification of protein clusters from vOTUs of global deep-sea RNA viruses. vOTUs, viral operational taxonomic units; ORFs, open reading frames. (B) Proportion of protein clusters of deep-sea vOTUs homologous to the known viral proteins in NCBI Viral RefSeq and IMG/VR v3 databases. (C) The distribution of protein clusters of deep-sea RNA viruses in three oceans and four ecosystems. The numbers indicate the quantity of protein clusters of RNA viruses. (D) The metabolic pathways mediated by putative viral genes of deep-sea RNA viruses based on the KEGG pathway database. (E) The relative abundance of sulfur metabolism genes encoded by deep-sea RNA viruses in different ecosystems. The genes encoded sulfate/thiosulfate transport system ATP-binding protein, adenylylsulfate kinase, sulfate adenylyltransferase subunit 2, phosphoadenosine phosphosulfate reductase, sulfite reductase (NADPH) hemoprotein beta-component, sulfate adenylyltransferase subunit 1, 5′-bisphosphate nucleotidase, sulfate/thiosulfate transport system permease protein, sulfate/thiosulfate transport system permease protein and sulfur-oxidizing protein.