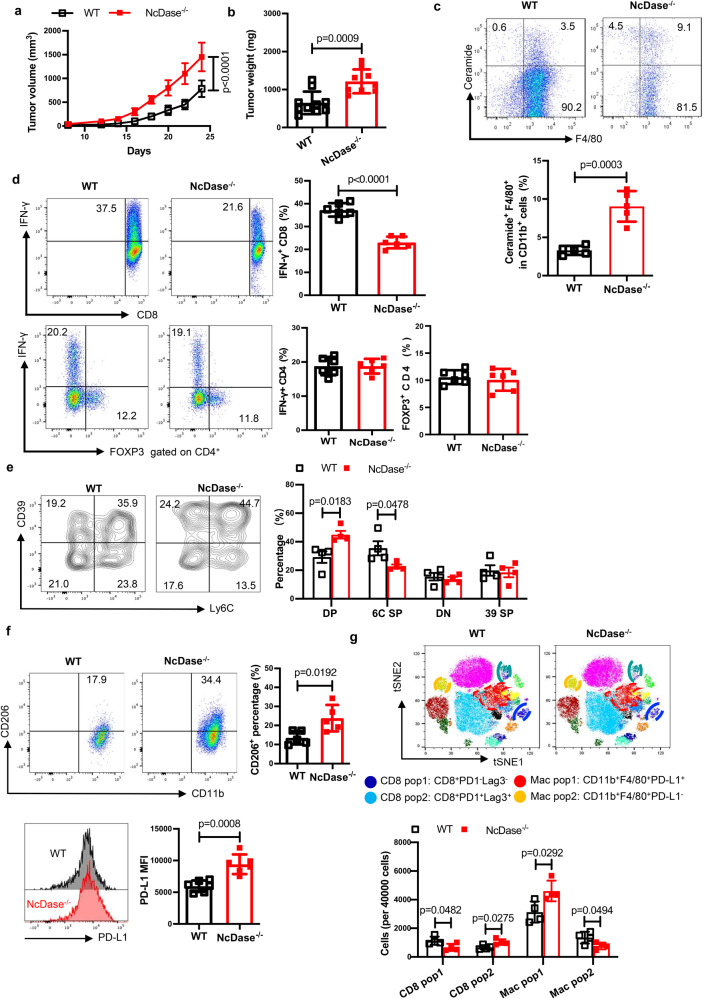
Fig. 8. NcDase is critical for obesity-promoted breast tumor growth.
WT and NcDase−/− mice on the HFD for 4 months were injected with EO771 mammary tumor cells (0.5 × 106) into mammary fat pad. a Tumor growth was monitored by measuring tumor size every 2 days for 24 days. b EO771 tumor weight on 24 days after tumor injection in mice with HFD. a, b n = 10 mice (WT) or 9 mice (NcDase−/−). c FACS analysis of levels of ceramide in CD11b+ F4/80+ TAMs isolated from WT and NcDase−/− mice bearing EO771 tumors. n = 5 independent biological samples. d Representative dot plots and frequencies of CD4+ IFN-γ+, CD4+ Foxp3+ or CD8+ IFN-γ+ T cells in TILs isolated from HFD-fed WT and NcDase−/− mice bearing EO771 tumors. n = 6 independent biological samples. e, f Representative dot plots and frequencies of Ly6C+CD39+ on CD8+ T cells (e, n = 4 independent biological samples), or CD206+ (n = 5 independent biological samples.), PD-L1+ (n = 6 independent biological samples.) on TAMs (f) in TILs isolated from HFD-fed WT and NcDase−/− mice bearing EO771 tumors. g Dot plot representation of tSNE analysis and 40,000 cells analysis showing different clusters that enable the distinction of exhausted CD8+ T cells and macrophages in TILs isolated from HFD-fed WT and NcDase−/− mice bearing EO771 tumors. n = 4 independent biological samples. Statistical comparisons were performed using two-tailed unpaired t-test (a, b, c, d, e), two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (e, g), Error bars indicate mean ± SD. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.