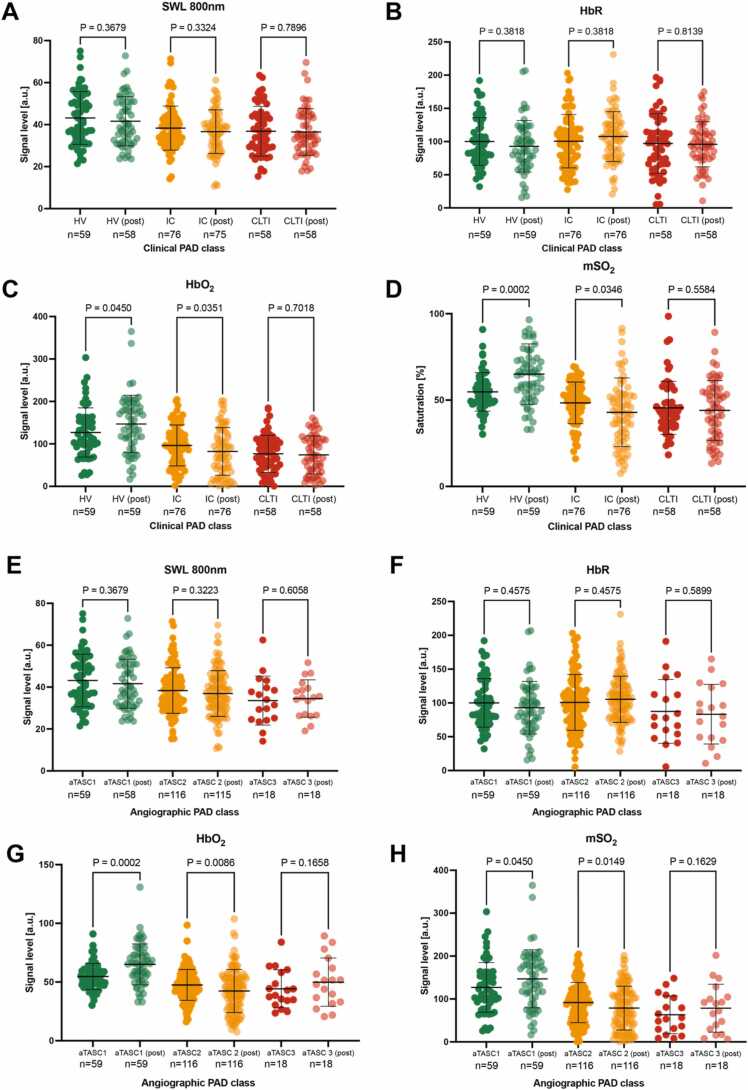
Fig. 7.
Exercise induced changes to optoacoustic signals. A-D Distribution of quantitative SWL 800 nm and spectral unmixed deoxygenated hemoglobin (HbR), oxygenated hemoglobin (HbO2) and multispectral unmixing derived oxygenation (mSO2) signals before and after exercise. The patients were grouped based on the clinical disease severity (HV; no clinical PAD symptoms, normal ankle-brachial-index (ABI) and palpable foot pulses; IC; combined Fontaine IIa: claudication at a distance > 200 m and IIb: claudication at a distance < 200 m; CLTI; combined Fontaine III: rest pain, mostly in the feet and IV: necrosis and/or gangrene of the limb). E-H Distribution of quantitative SWL 800 nm and spectral unmixed deoxygenated hemoglobin (HbR), oxygenated hemoglobin (HbO2) and multispectral unmixing derived oxygenation (mSO2) signals before and after exercise. The patients were grouped based on the angiographic disease severity (aTASC; aTASC1: included as healthy volunteer (HV) with no arteriosclerotic findings in angiography, aTASC 2: assumption of collateralization due to mild findings in aortoiliac (AI) or femoropopliteal (FP) vessel section, aTASC 3: assumption of poor collateralization due to severe AI findings). Dots indicate individual datapoints from patients, error bars indicate mean±SD.