Figure 1.
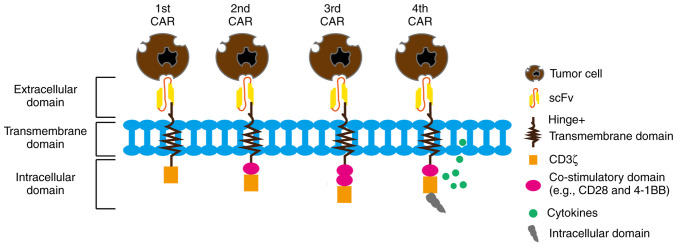
CAR structures include an extracellular antigen binding domain, a hinge region, a transmembrane domain and one or more intracellular signaling domains. The first-generation CAR consists of a CD3ζ signaling domain. Based on the understanding of the importance of co-stimulatory domains for durable therapy, the second-generation CAR was developed with an additional co-stimulatory domain linked to the CD3ζ intracellular signaling domain. The third-generation CAR includes two co-stimulatory domains linked to the CD3ζ signaling domain. The fourth-generation CAR introduces an additional intracellular domain that co-expresses certain small molecules (such as IL-12, IL-18 and programmed cell death protein 1), which can trigger cytokine-induced signaling or block signaling pathways that affect CAR-T cell function, aiming to improve therapeutic effects. CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; scFv, single-chain antibody.