Figure 1. Identified circuits within the PAG, RVM, and SC.
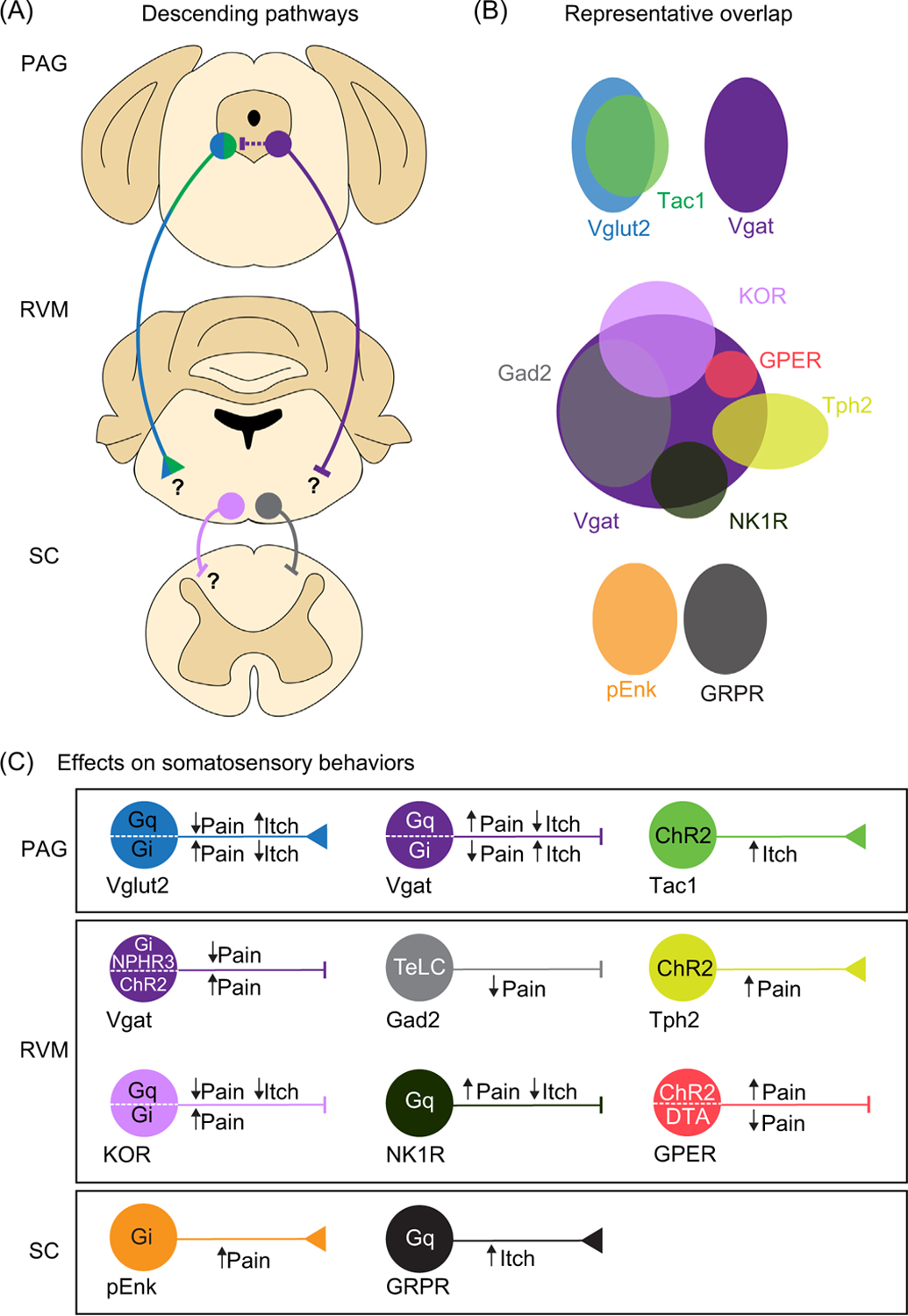
(A) An overview of the major components of descending modulatory pathways for nociception including the PAG, RVM, and SC. (B) Representative genetic overlap of PAG, RVM, and SC neuronal populations in the modulation of nociception and pruriception. Color codes in A are described in further detail. (C) Summary of effects of cell type-specific manipulations in the descending modulatory axis. Abbreviations: ChR2, channelrhodopsin-2; DTA, diphtheria toxin A; Gad2, glutamate decarboxylase 2; Gi, hM4Di, Gi-coupled human M4 muscarinic DREADD; GPER; G protein-coupled estrogen receptor; Gq, hM3Dq, Gq-coupled human M3 muscarinic designer receptor exclusively activated by designer drug (DREADD); GRPR, gastrin-releasing peptide receptor; KOR, kappa-opioid receptor; NK1R, neurokinin 1 receptor; PAG, periaqueductal gray; pENK, proenkephalin; RVM, rostral ventromedial medulla; SC, spinal cord; Tac1, tachykinin 1; TeLC, tetanus toxin light chain; Tph2, tryptophan hydroxylase 2; Vgat, vesicular GABA transporter; Vglut2, vesicular glutamate transporter 2.
