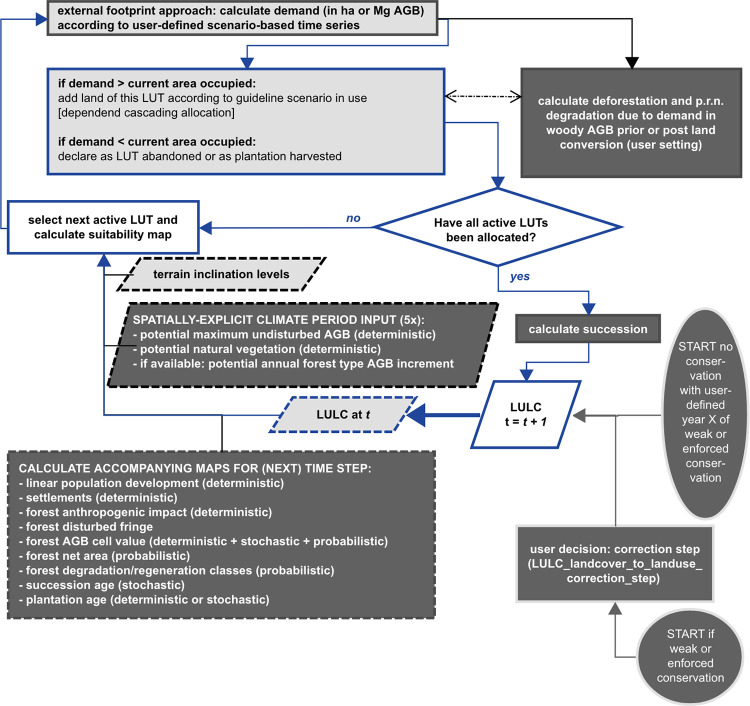
Fig 2. LPB-RAP module LULCC_basic allocation procedure.
The flowchart presents the LULCC_basic allocation based on the redesigned PLUC model engine’s basic functionality (blue). The extended LPB-RAP concept includes a variety of adapted (light grey) or new (dark grey) simulation components. These are new inputs and accompanying maps, allocation rules per guideline scenario and user settings, as well as differentiated succession modeling based on the provided baseline scenario information. The cascading allocation for a restriction policy measure in LULCC_basic is steered within the available landscape extents, LUTs and slope classes (restricted and excluded areas, excluded LUTs and inaccessible terrain cannot be used). Accessible terrain is differentiated into favorable and difficult terrain. Cascading allocation refers to coding where the next level of accessible terrain, i.e., the next pool of available cells, is only used if there is still unsatisfied demand. The cascading allocation for weak conservation is: (1) favorable terrain outside restricted areas, (2) difficult terrain outside restricted areas, (3) favorable terrain inside restricted areas, and (4) difficult terrain inside restricted areas. For enforced conservation, the allocation excludes restricted areas, thereby the allocation occurs in the order (1) favorable terrain outside restricted areas, (2) difficult terrain outside restricted areas. For the no conservation scenario, the cascading allocation is partitioned into (1) favorable terrain landscape-wide and (2) difficult terrain landscape-wide.