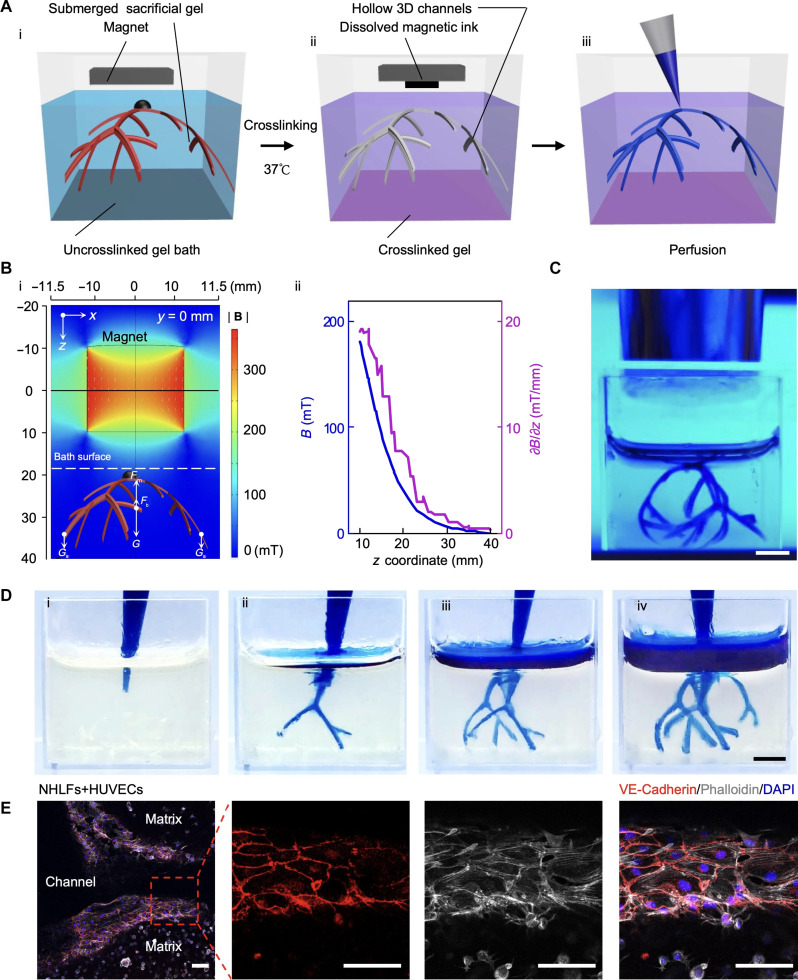
Fig. 5. Magnetically driven transformation to create bioscaffolds with 3D branching vascular channels.
(A) Scheme showing the steps to fabricate bioscaffolds with 3D branching vascular channels by magnetically driven transformation strategy. (i) Flat sacrificial gelatin precursor immersed in the uncrosslinked gel bath is transformed into 3D geometry when a magnet is applied. (ii) After crosslinking the gel bath under UV, the crosslinked scaffold is placed at 37°C with the magnet still placed on top to dissolve gelatin and remove the dissolved magnetic ink. (iii) Scheme showing the perfusion of the generated scaffold. (B) Magnetic field distribution analysis. (i) Finite element analysis of the magnetic field distribution caused by the applied magnet. (ii) Magnetic field distribution across the z coordinate. (C) UV crosslinking of the scaffold after the sacrificial precursor was transformed into a 3D morphology. Scale bars, 5 mm. (D) Scaffold perfusion with a blue dye demonstrated from (i) to (iv). Scale bars, 5 mm. (E) Immunostaining for VE-cadherin (Red), phalloidin (gray), and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue) in the fibrin scaffold with HUVECs lining the channel wall and NHLFs within the fibrin matrix. Scale bars, 100 μm.