Figure 2.
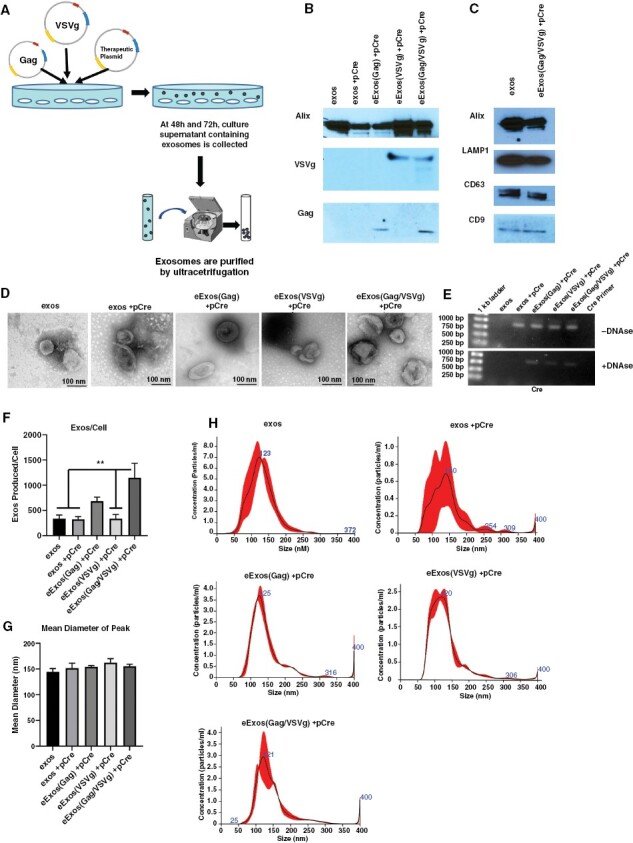
Engineered exosomes express viral factors and package plasmids. (A) Generation and isolation of eExos was achieved by transfection of HEK293T cells with plasmids containing cDNA of viral proteins and the cDNA of a therapeutic gene or reporter (Cre) gene, followed by collection and ultracentrifugation of cell supernatant. (B) Western blot demonstrates eExos expression of Gag and/or VSVg (10 μg protein loaded per lane). (C) Western blot for common exosomal markers LAMP1, CD63, CD9, and endosomal pathway protein Alix shows expression in both unmodified HEK293T exosomes (exos) and eExos (10 μg protein loaded per lane). (D) Electron microscopy of exosomes. eExos structurally resemble unmodified exos. Pictures taken at 300 000×, scale bar is 100 nm. (E) eExos were transfected with Cre plasmid. Exosomes were isolated and were treated with or without Turbo DNAse. DNA was isolated from exosomes and subjected to Cre-specific PCR. (F) The number of exos/cell, (G) mean diameter, number of exos/cell, and (H) standard distribution of peak sizes using nanoparticle tracking analysis. The vesicle size ranged from 50 to 200 nm with a peak size around 150 nm. **P < .01. Data shown are representative of >3 separate experiments. Error bars representing the SEM were calculated using Prism and are derived from triplicate experimental conditions.
