Figure 4.
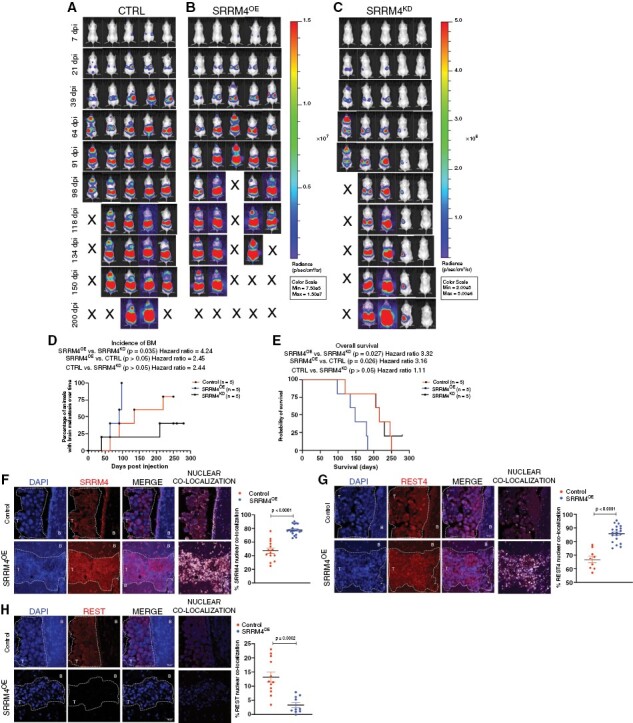
Enhanced SRRM4 expression augments breast-to-brain metastatic competency and contributes to worse overall survival in vivo: representative images of bioluminescent imaging (BLI) for brain metastasis and overall tumor load, post-intracardiac injection of SKBR3 (A) control scramble (CTRL), (B) SRRM4OE, and (C) SRRM4KD cells in vivo (n = 5 per group). BLI intensity scale was normalized in control and SRRM4OE groups (Min: 7.5e5; Max: 1.5e7). Scale for SRRM4KD group was reduced (Min: 2e5; Max: 5e6) since mice showed lower overall tumor load, and any incidence of BMs in these animals would go unnoticed if scale was as per groups A and B. (D) Graphical comparison of BM incidence in animals over time (n = 5 per group). Mice in SRRM4OE group showed accelerated incidence of BMs compared to SRRM4KD group (P = 0.035, HR = 4.24) and SKBR3ctrl group (P > 0.05, HR = 2.45). (E) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis in SKBR3ctrl, SRRM4OE, and SRRM4KD xenografted mice (n = 5 per group). Mice in SRRM4OE group (blue line) showed significantly worse overall survival compared to SKBR3ctrl cells (P = 0.026, HR = 3.16), and SRRM4KD cells (P = 0.027, HR = 3.32) (Statistics—Log-Rank test). Representative IF images for expression and comparison of nuclear (F) SRRM4, (G) REST4, and (H) REST in brain-metastatic lesions from SKBR3ctrl and SRRM4OE xenografted mice (magnification ×40; scale 30 µm). Graphs show comparison of percent nuclear SRRM4, REST4, and REST in individual cells for both groups. T = tumor, B = brain tissue.
