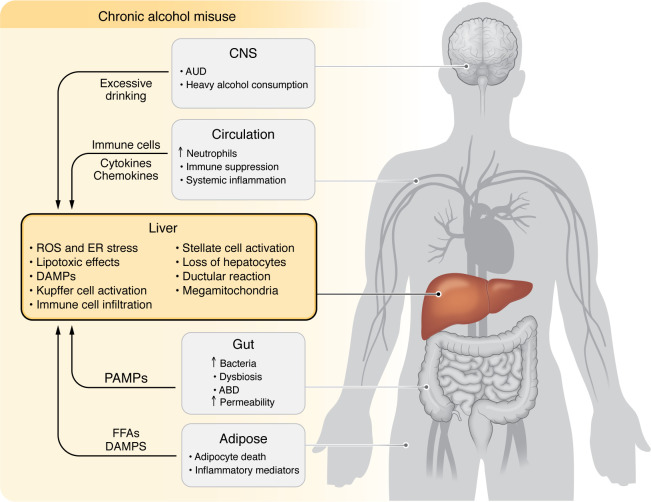
Figure 2. Pathogenesis of and interorgan crosstalk contribution to ALD.
Excessive alcohol intake directly induces hepatocellular damage via multiple mechanisms. The crosstalk with several other organs, including brain-liver, gut-liver, and adipose-liver crosstalk, also contributes to ALD pathogenesis. Excessive alcohol consumption profoundly affects the immune system and immune cells, which also contributes to ALD progression. ABD, alcohol-associated bowel disease; AUD, alcohol use disorder; DAMP, damage-associated molecular pattern; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern; FFA, free fatty acid.