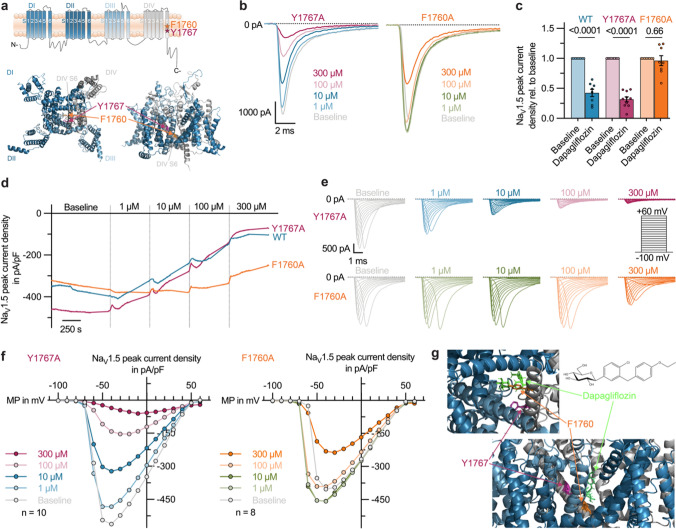
Fig. 4.
Investigation of the susceptibility of molecular drug binding sites of NaV1.5 to dapagliflozin. a Three-dimensional visualization of the NaV1.5 channel based on the recently revealed cryo-EM structure of the rat NaV1.5 ortholog (PDB ID: 6UZ0 [18]). The four repetitive domains of this pseudo-tetramer, each harboring 6 segments (S1–6) are visualized in different shades of blue and the pore-lining mutants F1760 and Y1767 located in the S6 segment of the fourth domain (DIV S6) are highlighted in orange and purple, respectively. b Representative NaV1.5 current traces, recorded with Automated Patch Clamp (APC) from Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells transiently transfected with SCN5A pore mutants Y1767A (left) and F1760A (right) during a gradual increase of the dapagliflozin concentration (1–300 µmol/L). c NaV1.5 peak current densities relative to baseline values, measured with APC in CHO cells heterologously expressing SCN5A wild-type (WT) or pore mutants Y1767A and F1760A at -20 mV under baseline conditions and after administration of dapagliflozin (100 µmol/L; n = 8–10). d Time course of NaV1.5 peak current densities, recorded with APC from CHO cells transfected with SCN5A WT, Y1767A or F1760A during gradual increase of the dapagliflozin concentration (1–300 µmol/L). e Representative families of sodium current traces, recorded with APC from CHO cells transfected with SCN5A Y1767A or F1760A during stepwise increase of dapagliflozin concentration (1–300 µmol/L). The pulse protocol is depicted as inset. f Current–voltage-relationship of NaV1.5 peak current densities, recorded with APC from CHO cells transfected with SCN5A Y1767A (left) or F1760A (right) at baseline and after stepwise administration of dapagliflozin (1–300 µmol/L) (n = 8–10; MP, membrane potential). g Hypothetical docking of dapagliflozin into the NaV1.5 channel pore. The regions of the excerpts are indicated in (a) as dashed squares. Data are provided as mean ± SEM and P-values were derived from paired Student’s t-tests