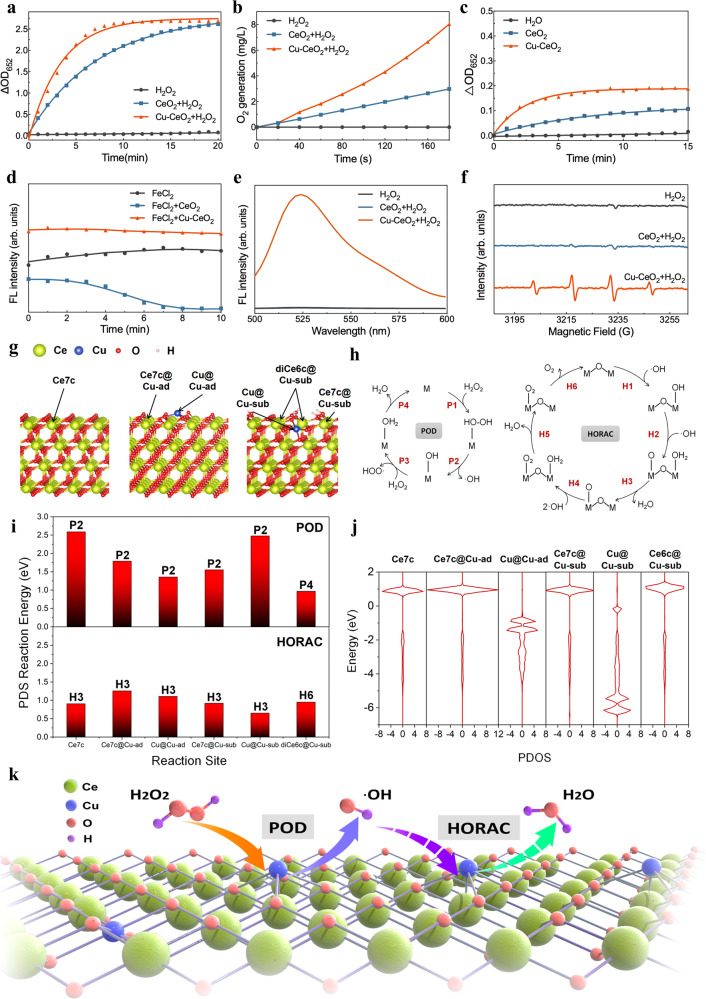
Fig. 3. Catalytic activities and mechanism of CeO2 and Cu-CeO2 nanozymes.
a Time-dependent optical density change at 652 nm of 3,3’, 5,5’-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) in POD reactions. b Time dependent oxygen generation in CAT reactions. c Time dependent optical density change at 652 nm of TMB in OXD reactions. d Time dependent fluorescent intensity of 2,7-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH) in HORAC reactions. e Fluorescent spectra of DCFH after 10 min reaction with H2O2 and different nanozymes. f Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) spectra of DMPO-OH after 10 min reaction with H2O2 and different nanozymes. g The calculated model of pristine CeO2 (left), CeO2 with Cu3c added on the 3O atoms on the surface (Cu-ad, middle) and CeO2 with a Ce atom substituted by Cu (Cu-sub, right). The 6 possible reaction sites are highlighted with a tagged arrow. h The reaction mechanism of POD and HORAC process, M indicates the metal sites. i The calculated PDS reaction energy of POD and HORAC processes for different reaction sites with the exact PDS labeled above the bar. j The calculated PDOS, i.e., the d and f band summation of different reaction centers. k The proposed mechanism of regulation of catalytic activities by Cu-CeO2 single-site nanozyme. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.