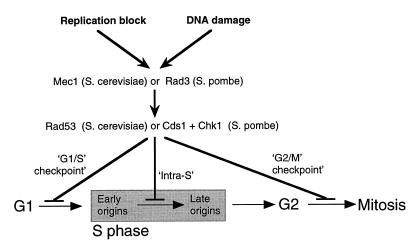
Fig. 2. Schematic overview of checkpoint functions. Two triggers of the checkpoint machinery (incomplete replication and DNA damage) lead to activation of the checkpoint kinases. Depending on where the cell happens to be in the cell cycle, this can cause cell cycle arrest via either the ‘G1/S’ checkpoint, the ‘intra-S’ checkpoint or the ‘G2/M’ checkpoint.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.