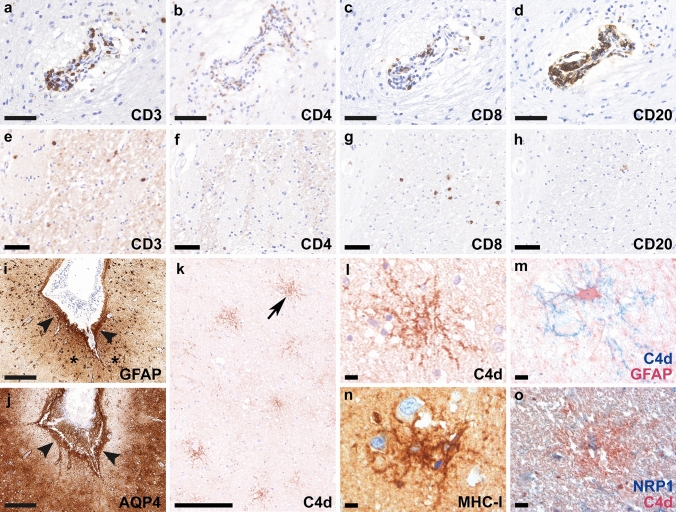
Fig. 1.
Neuropathological findings of anti-GFAP meningoencephalitis – autopsy case #1 The inflammatory reaction is characterized by perivascular cuffs with abundant CD3+ (a), CD4+ (b) and CD8+ T cells (c), as well as CD20+ B cells (d). In the brain parenchyma, CD3+ (e) and CD8+ T cells (g) were more abundant compared to CD4+ (f) and CD20+ (h) lymphocytic infiltrates. Reactive gliosis in the depth of the sulci (i, asterisks, GFAP) is present subjacent to meningeal lymphocytic infiltrates (i, arrowheads, GFAP). AQP4 is upregulated and mainly found in subpial astrocytes (j, arrowheads). C4d indicates complement deposition on astrocytes (k, arrow in k enlarged in panel l), confirmed with double labeling for C4d (blue) and GFAP (red) (m). MHC class I molecules are upregulated in some astrocytes (n). Deposition of C4d on NRP1-positive glial cells is confirmed with the double labeling for NRP1 (blue) and C4d (red) (o). Scale bars a–d, i, j 100 µm; e–h 50 µm; k 500 µm; l-o 25 µm. AQP4 aquaporin 4, CD cluster of differentiation, C4d complement split product 4d, GFAP glial fibrillary acidic protein, MHC-I major histocompatibility complex class I, NRP1 neuropilin 1