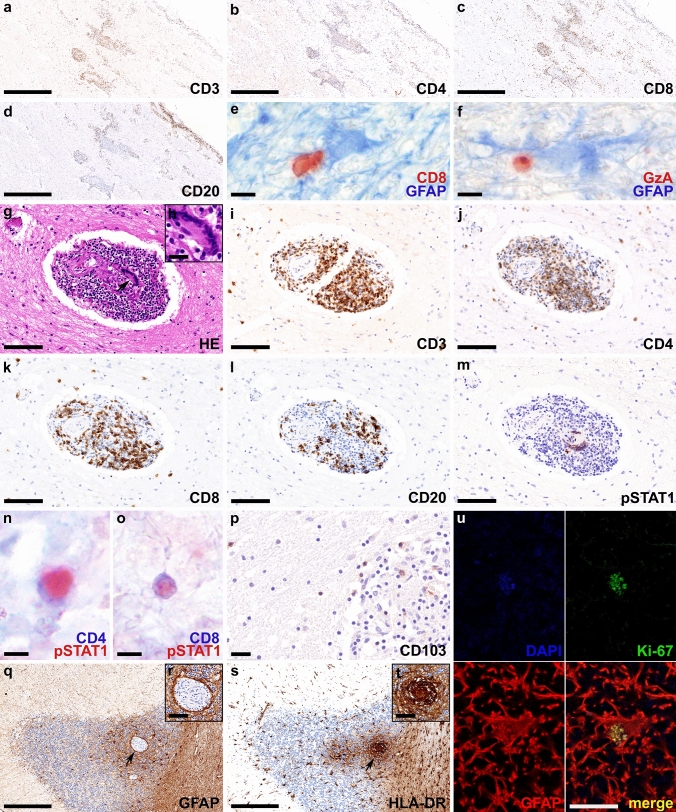
Fig. 4.
Neuropathological findings of anti-GFAP meningoencephalomyelitis – autopsy case #2 In the chiasma opticum numerous CD3+ (a), CD4+ (b) and CD8+ T cells (c) and CD20+ B cells (d) are present in the leptomeninges and around vessels. Parenchymal CD8+ T cells (red) are found in close proximity to GFAP positive astrocytes (blue) (e). Some of these T cells express granzyme A (red) (f). The perivascular granulomas contain multinucleated giant cells of the Langhans type (arrow in g enlarged in inset h), and a high number of CD3+ (i), CD4+ (j) and CD8+ T cells (k), and less CD20+ B cells (l). pSTAT1, a marker for interferon signaling, is strongly upregulated in nuclei of multinucleated giant cells (m) and CD4+ (n) and CD8+ T lymphocytes (o). CD103+ tissue resident memory T cells are present in the granulomas as well as in the brain parenchyma (p). In the cerebellum, granulomas are evident in the cortex with prominent astrogliosis (arrow in q enlarged in inset r) with well-preserved astrocytic processes (r) and microglia activation (arrow in s enlarged in inset t). The proliferation marker Ki-67 (green) is expressed in the nucleus (blue; DAPI) of some astrocytes (red; GFAP) (u). Scale bars a-d, q, s 250 µm; e, f, n, o 6 µm; g, i-m 50 µm; h, p, r, t 10 µm; u = 5 µm. AQP4 aquaporin 4, CD cluster of differentiation, DAPI 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, GFAP glial fibrillary acidic protein, GzA granzyme A, H&E hematoxylin & eosin, HLA human leukocyte antigen, pSTAT1 phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 1