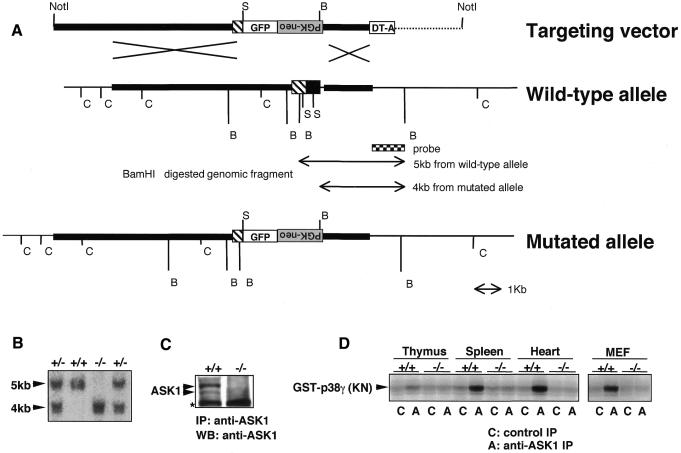
Fig. 1. Generation of ASK1–/– mice by gene targeting. (A) Restriction map around the first coding exon of ASK1 gene and structure of the targeting vector. Homologous regions for recombination are drawn by thick lines in the restriction map. Coding and non-coding regions of ASK1 gene are represented by filled and hatched boxes, respectively. The genomic fragment used as a probe for Southern blot analysis for precise determination of recombination in ES cells and genotypes of mice is indicated below the map. The expected mutant allele and polymorphic fragments for genotyping from BamHI-digested genomic DNA are also indicated. GFP, coding sequence for green fluorescence protein followed by bovine growth hormone poly(A) signal; PGK-neo, coding sequence for neomycin phosphotransferase flanked by the phosphoglycerate kinase promoter and poly(A) signal; DT-A, diphtheria toxin A gene driven by MC1 promoter; C, SacI; S, SmaI; B, BamHI. Inverted characters for ‘PGK-neo’ indicate an insertion of the PGK-neo cassette in a reverse orientation. (B) Southern blot determining homologous recombination within the ASK1 locus of genomic DNA extracted from tails of F2 mice. BamHI digestion generated hybridized bands of the expected sizes for wild-type (5 kb) and mutant (4 kb). (C) Western blot demonstrating the absence of ASK1 protein in ASK1–/– MEFs. MEFs were immunoprecipitated with anti-ASK1 antiserum (DAV) and subsequently subjected to immunoblotting with anti-ASK1. Asterisk indicates non-specific reactions. (D) Immune complex kinase assay confirming the absence of ASK1 kinase activity in ASK1–/– mice. Extracts from indicated tissues and cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-ASK1 or control serum. Immune complex was incubated with GST–MKK6, and a kinase activity was then measured with the substrate GST–p38 γ(KN) which resulted in a phosphorylated image of GST–p38 γ (KN).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.