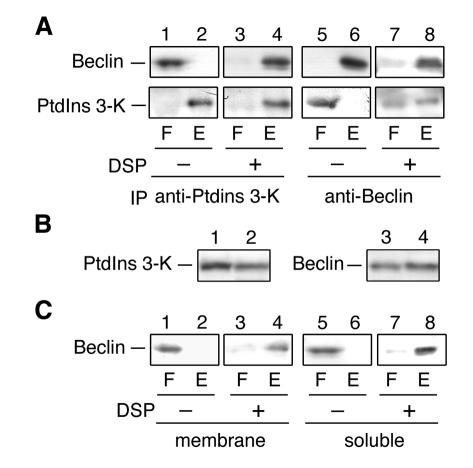
Fig. 2. Cross-linking of Beclin and PtdIns 3-kinase. (A) Total cell lysates were treated with DSP (lanes 3, 4, 7 and 8) or its solvent, dimethylsulfoxide (lanes 1, 2, 5 and 6), at 4°C for 2 h. Proteins were solubilized with SDS and subjected to immunoprecipitation using protein A-immobilized anti-PtdIns 3-kinase (PtdIns 3-K) (lanes 1–4) or Beclin (lanes 5–8) antibodies. Immunoprecipitates were eluted with 1× SDS sample buffer (62.5 mM Tris–HCl pH 6.8, 2% SDS, 10% glycerol, a trace amount of Bromophenol blue). After treatment with 5% 2-mercaptoethanol, proteins were separated by SDS–PAGE, followed by detection by immunoblotting with anti-Beclin (upper panels) and anti-PtdIns 3-kinase (lower panels) antibodies. (B) Cell lysates prepared from HeLa cells were subjected to subcellular fractionation by centrifugation at 100 000 g for 1 h. The membrane (lanes 1 and 3) and supernatant (lanes 2 and 4) fractions were subjected to SDS–PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with anti-PtdIns 3-kinase (lanes 1 and 2) and anti-Beclin (lanes 3 and 4) antibodies. (C) Membrane (lanes 1–4; 100 000 g, 30 min, pellet) and soluble fractions (lanes 5–8; 100 000 g, 30 min, supernatant) prepared from HeLa cells were treated with DSP (lanes 3, 4, 7 and 8) or dimethylsulfoxide (lanes 1, 2, 5 and 6). Proteins were solubilized with SDS and subjected to immunoprecipitation using protein A-immobilized anti-PtdIns 3-kinase antibodies. Immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS–PAGE under a reducing condition, followed by detection by immunoblotting with Beclin antibodies. F and E indicate flow-through and elute fracions, respectively.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.