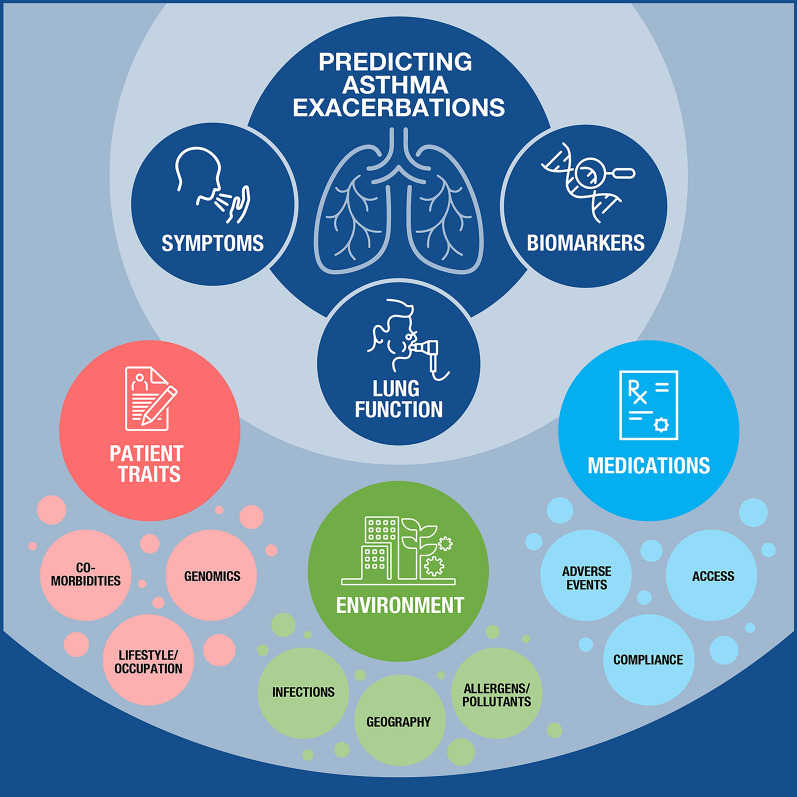
Fig. 1.
The constellation of factors influencing the asthmatic patient’s journey that may be analyzed using artificial intelligence to augment clinical decision-making. Patients with asthma present a unique collection of factors that influence their disease severity and outcome. The cornerstones of traditional patient management consist of assessments of pulmonary function (i.e., spirometry measuring lung capacity and FEV1), biomarker levels (e.g., blood eosinophils, IgE, FeNO), and patient-reported symptoms (e.g., cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, sleep). However, a myriad of factors together influence the individual patient’s risk of asthma exacerbation and disease progression, including both intrinsic factors such as genomics, comorbidities, and allergic status, and extrinsic factors such as occupational and environmental exposures, access to the healthcare system and medications, and geography. Because asthma exacerbations are complex and multidimensional phenomena, the use of artificial intelligence may better predict such events if proper inputs (including intrinsic and extrinsic factors) are provided to train, validate, and test next-generation treatment algorithms. IgE immunoglobulin E, FeNO fractional exhaled nitric oxide, FEV1 forced expiratory volume in 1 s