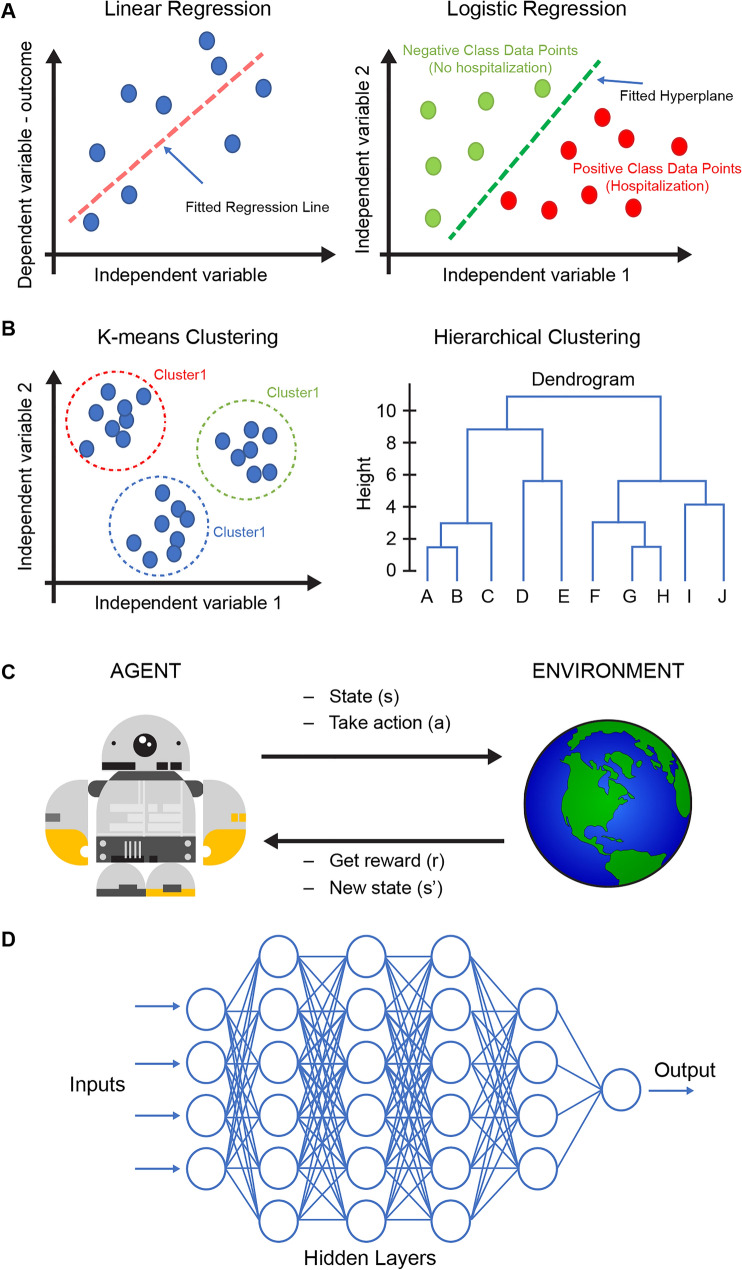
Fig. 2.
Supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement, and deep learning algorithms. a Linear regression and logistic regression are among many supervised learning algorithms and are trained on labeled data. The label can be either a continuous outcome (linear regression) or a category (logistic regression). b K-means clustering and hierarchical clustering are examples of unsupervised learning algorithms and use unlabeled data to discover hidden patterns and data clusters. The output of the supervised learning can be the clusters’ information, a dendrogram, or other visuals that highlight notable patterns within the data. c Reinforcement learning algorithms train an agent to find the optimal succession of actions that optimize a given task. The agent acts within an environment, according to defined rules and a reward system, and through trial and error, the agent explores the whole solution space and eventually identifies the optimal solution. d Deep learning models are composed of multiple layers of artificial neural networks and can be trained to predict continuous and categorical variables, using both structured (i.e., tables) and unstructured data (i.e., images, time series)