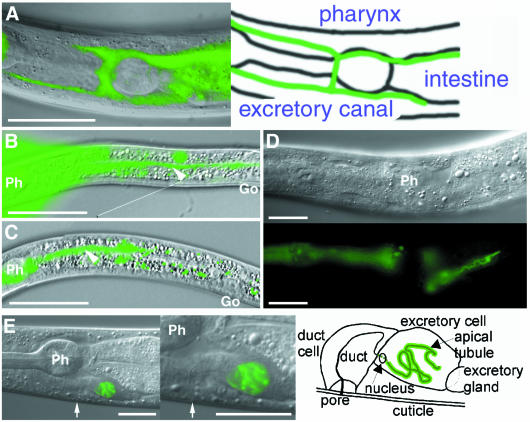
Fig. 4. Effect of exc-5 overexpression on structure of the excretory canal. (A) Expression of exc-5 is visualized using exc-5::GFP in exc-5(km508). The photo shows the ventral view. The dotted fluorescence results from the autofluorescence of gut granules. (B) L1 unc-119(e2498) larva with exc-5 5′::GFP and pDP#MM016B (unc-119). The excretory canal is visualized using exc-5 5′::GFP expression. High fluorescence in pharynx (Ph) is overexposed to show expression extending throughout the narrow canal (arrowhead). Go, gonad. (C–E) The excretory canal is visualized using exc-5::GFP expression in unc-119(e2498) with exc-5::GFP and pDP#MM016B. (C) The photo shows a truncated posterior excretory canal (arrowhead) from a left lateral aspect in L1 larva. (D) The photos show a shortened posterior excretory canal in L4 larva. Upper and lower panels show Nomarski and epifluorescence images, respectively. The animal has a convoluted tubule in the excretory canal. exc-5::GFP is predominantly expressed at the lumenal (apical) surface of the cell. (E) The photos show a large non-cystic cell body in a mosaic L4 larval animal expressing exc-5::GFP in the excretory canal. The middle panel shows the cell body at high magnification. The arrow indicates a pore connecting the excretory canals to the surface of the animal. GFP expression is seen at the apical surface of the cell. The right panel shows a diagram of the middle panel. Scale bars, 20 µm.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.