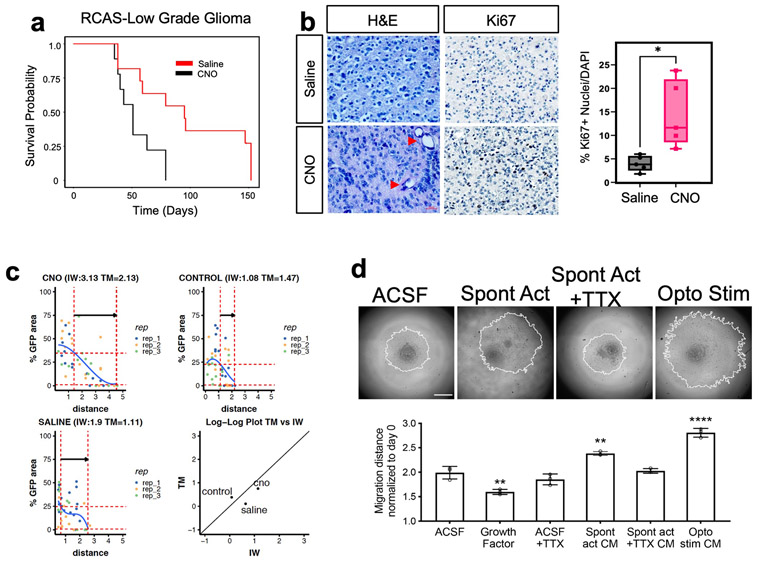
Extended Data Figure 1. Contralateral activity drives glioma progression and infiltration.
a. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of RCAS-Ntva tumors treated with saline (medianSaline= 95 days, n = 11) or CNO (medianCNO = 51 days, n = 9) showing significantly faster morbidity in CNO treated RCAS tumors (Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test, Chisq = 6.456, df = 1, p-value = 0.0111, CNO/Saline HRlog-rank= 2.768, 95% CI = 0.9770 to 7.945). b. H&E staining of RCAS-Ntva tumors samples revealed high grade characteristics in CNO treated tumor groups (red arrows). Ki67 staining proliferation in CNO treated mice versus saline treated mice. Quantification is derived from n=5 mice from CNO (mean = 14.51%, SD = 7.076%) and Saline (mean = 4.017%, SD = 2.179%) groups and determined by Welch’s unpaired t-test (P-value = 0.0276, t = 3.228, df = 4.441). c. Mathematical modeling of glioma infiltration as a function of tumor mass. Blue line is the smoothed data points using piecewise-cubic splines; red horizontal dashed lines are the 0.8 pmax and 0.02 pmax glioma cell density of the maximum smoothed cellular density (pmax ). Red vertical lines are the intersecting distance points of the red horizontal lines with smoothed blue line, which is used in calculating infiltrating width (IW). Black arrow shows the IW. Log-log plot shows the dependence of IW and tumor mass (TM). Analysis was performed at the p30 timepoint on CTL n = 3, Saline n = 3, CNO n = 3; samples from individual biological replicates are color coded. d. Glioma 3D spheroid migration assay, measuring glioma infiltration after treatment with growth factor media, conditioned media (CM) from spontaneously active cortical explants, spontaneously active cortical explants silenced with TTX (10μm) or optogenetically stimulated cortical explants (channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2)-expressing deep layer cortical projection neurons), in comparison to ACSF control. Data are plotted as median (center line), IQR (box limits) and minimum and maximum values (whiskers) (b).