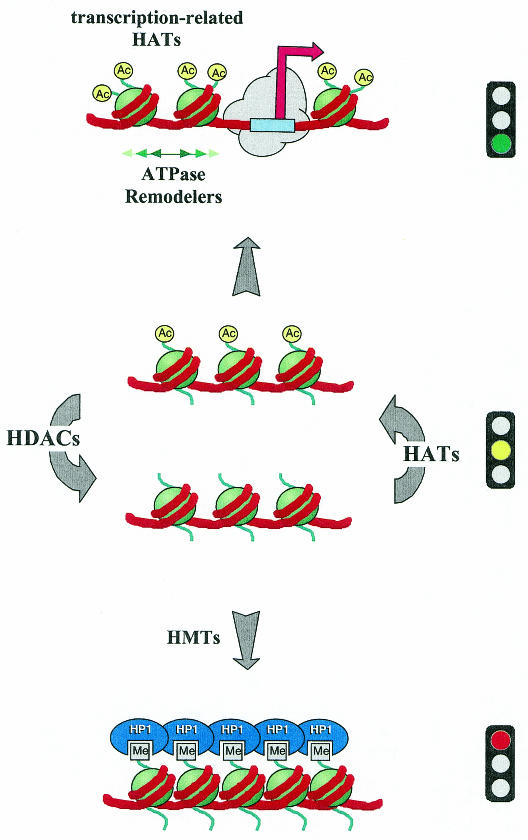
Fig. 1. The histone acetylation switch. Targeted HAT and HDAC activities negotiate the acetylation status of chromatin. Acetylation establishes a structure that permits ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling factors to open promoters. Deacetylation, frequently followed by histone methylation, may form a solid base for highly repressive structures, such as heterochromatin. Acetylated histone tails are shown as yellow circles. Methylations are indicated as gray rectangles. HAT, histone acetyltransferase; HDAC, histone deacetylase; HMT, histone methyltransferase; HP1, heterochromatin protein 1.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.