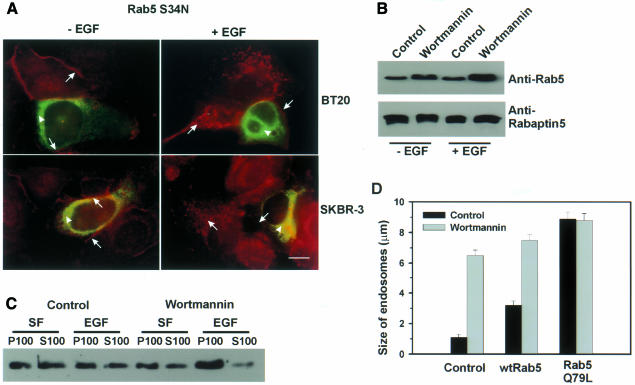
Fig. 4. Wortmannin regulates intracellular trafficking by activating Rab5. (A) Suppression of wortmannin-induced endosome enlargement by Rab5 S34N. BT20 and SKBR-3 cells were transfected with mutant Rab5 S79N for 48 h. The cells were then treated with wortmannin and stimulated with EGF for 30 min or not stimulated. Photographs are double exposures with EGFR localization in the red channel (arrows) and Rab5 localization in the green channel (arrowheads). Size bar = 20 µm. (B) The effects of wortmannin on the association of Rab5 and its effector Rabaptin5. BT20 cells were treated with wortmannin for 15 min or not treated, and then stimulated with EGF for 30 min or not stimulated. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with mouse anti-Rabaptin5 antibody, followed by agarose-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with mouse anti-Rab5 or anti-Rabaptin5 antibody. (C) The effects of wortmannin on the membrane association of Rab5. BT20 cells were subcellularly fractionated into soluble fraction (S100) and particulate fraction (P100) after treatment with wortmannin (100 nM) and EGF (30 min) as indicated. The subcellular fractions were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-Rab5 antibody as described in Methods. (D) The effects of wortmannin and Rab5 on the size of endosomes in BT20 cells. Experiments were performed as described for Figure 3B.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.