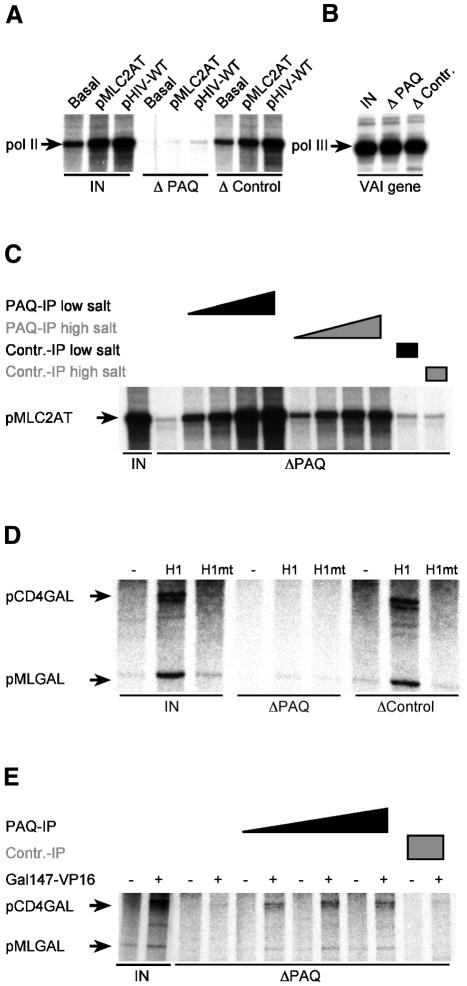
Fig. 1. PAQ-associated complex is a general factor in physiological transcription systems. (A) PAQ depletion (ΔPAQ) abolishes RNA polymerase II transcription in HeLa nuclear extracts (IN), whereas depletion with control antibody (ΔControl) does not affect formation of transcripts (pol II). (B) PAQ depletion is specific for RNA polymerase II. Formation of RNA polymerase III transcripts (pol III) is not influenced. (C) Capacity of PAQ-associated complex to restore transcription in depleted nuclear extracts is resistant to high salt washes, arguing for specificity of the procedure. Titration of the respective complexes was performed in a four-fold range. (D) and (E) PAQ-associated complex is essential for TATA-less and TATA-containing promoters driven by Gal4-VP16. (D) PAQ depletion (ΔPAQ) abolishes RNA polymerase II transcription in Jurkat nuclear extracts (IN). Transcription reactions were performed with pCD4GAL (TATA-less reporter) and pMLGAL (TATA-containing reporter) as templates in the absence (–) and presence (+) of 20 ng of activators Gal-VP16:H1 (H1) and Gal-VP16:H1F442P (H1mt), respectively. (E) PAQ-associated complex restores basal and activated transcription in depleted Jurkat nuclear extracts (ΔPAQ). Titration of the complex was achieved in a three-fold range in the absence (–) and presence (+) of Gal147-VP16.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.