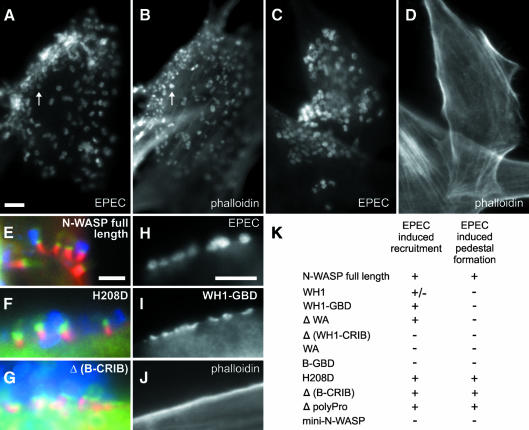
Fig. 4. EPEC pedestal formation depends on N-WASP. Infection of precursor (A, B) and N-WASP-defective cells (C–J) with EPEC. EPEC are shown in (A, C and H) and in blue in (E–G). F-actin is shown in (B, D and J) and in red in (E–G). GFP constructs are shown in (I) and in green in (E–G). EPEC (A, C)-induced formation of actin pedestals in precursor (B), but not in N-WASP-defective cells (D). Pedestal formation in N-WASP-defective cells was restored upon expression of GFP-tagged full-length N-WASP (E), N-WASP-H208D (F) and N-WASP-Δ(B-CRIB) (G), while N-WASP-WH1-GBD was recruited (I) by EPEC (H) without induction of actin pedestals (J). Bars (5 µm) in (A, E and H) are valid for (A–D), (E–G) and (H–J), respectively. For description of GFP fusion constructs see Figure 3K. (K) The recruitment to EPEC attachment sites and reconstitution of pedestal formation by the respective mutants are indicated.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.