Fig. 6.
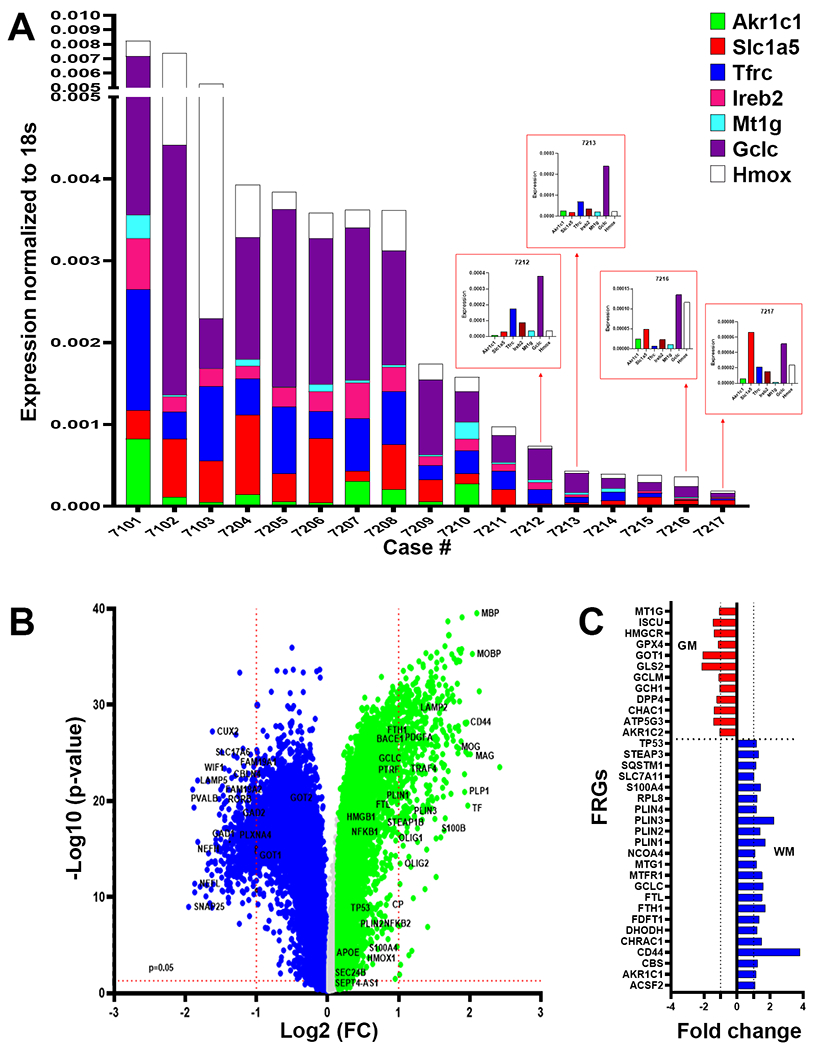
DM are enriched in markers of ferroptosis. (A) Analysis of white matter lesions from 17 cases enrolled in the ACT study diagnosed with dementia-related to microvascular brain injury (mVBI) or ADNC. Gene expression was variably enhanced for seven markers associated with distinct ferroptosis pathways (GCLC, HMOX1, TFRC, IREB2, MR1G, AKRC1c and SLC1A5) quantified by qRT-PCR and normalized to 18S rRNA. (B) Analysis of bulk RNAseq data set from the Allen Institute for Brain Science of gene expression in 110 cases enrolled in the ACT study diagnosed with a spectrum of mVBI or ADNC. Volcano plot of the p-value (−Log 10) and fold change of genes with significantly higher expression in white matter relative to gray matter (green; 21,879 genes) or gray matter relative to white matter (blue; 22,569 genes). A unique set of white matter-associated ferroptosis-related genes were significantly upregulated together with highly expressed genes linked to myelination. (C) Comparison of the fold expression changes for ferroptosis-related genes in white matter (blue) vs. gray matter (red).
