Figure 9. NK cells contribute to superior viral load control in PWD mice.
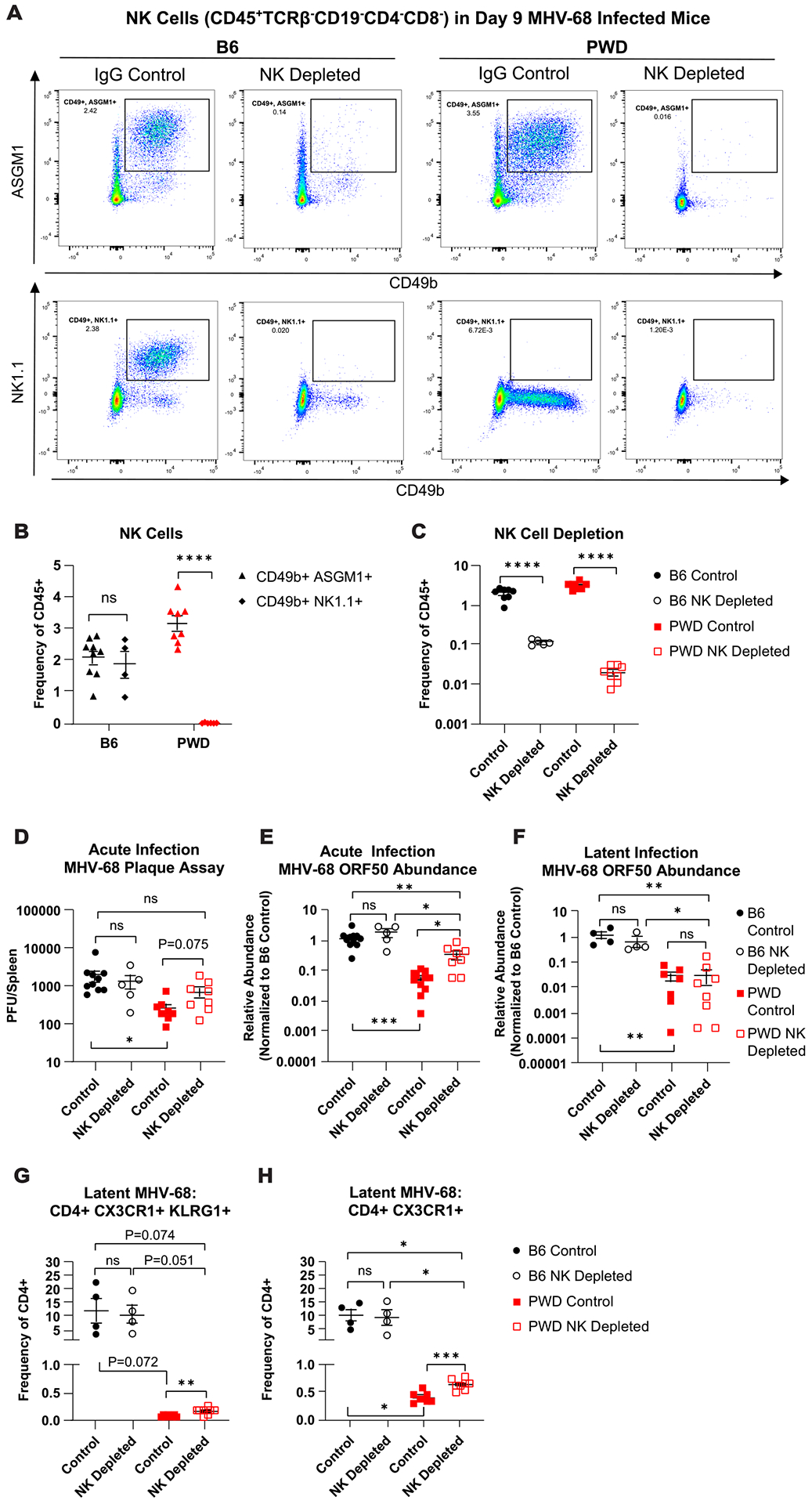
Female and male B6 and PWD mice were treated with anti-NK1.1 (acute n = 2F + 3M B6, latent n = 2F + 2M B6) or anti-ASGM-1 antibodies (acute n = 2F + 6M PWD, latent n = 6F + 2M PWD), respectively (NK depleted) or IgG isotype control antibodies (control) (acute n = 8F + 3M B6 and 4F + 8M PWD, latent n = 2F + 2M B6 and 5F + 2M PWD) and one day later infected with 104 PFU of MHV-68. Data shown are pooled from three independent experiments. At 9- (D9) and 35- (D35) days post infection, spleens were collected and processed for flow cytometry, qPCR, or infectious viral titration (see Materials and Methods). (A) Representative staining profiles of NK cell markers CD49b, NK1.1, and ASGM1 on CD45+TCRβ− CD19− CD4− CD8− cell populations in NK depleted or IgG control-treated D9 B6 and PWD mice. (B) Assessment of CD49b+ASGM1+ and CD49b+NK1.1+ NK cell populations in D9 MHV-68 infected B6 and PWD mice, represented as frequency of total CD45+ splenocytes. (C) NK cell populations (TCRβ− CD19− CD4− CD8− CD49b+ASGM1+) as frequency of CD45+ cells in D9 B6 and PWD NK depleted and IgG control mice. (D) Comparison of plaque forming units (PFU) between D9 B6 and PWD IgG control and NK depleted mice. Relative abundance of MHV-68 ORF DNA normalized to B6 IgG control, in B6 and PWD IgG control and NK depleted mice at (E) D9 and (F) D35, as assessed by qPCR. Assessment of ThCTL cells – (CD4+TCRβ+CD11b−CD19−) (G) CD4+CX3CR1+KLRG1+ and (H) CD4+CX3CR1+ at D35 in B6 and PWD IgG control and NK depleted mice. Significant differences between or within B6 and PWD mice, sexes pooled, given IgG control or NK depletion conditions were determined via unpaired T-tests, or Welch’s T-test in cases where the variance between groups was significantly different as calculated by an F test, and are indicated by the brackets where significant (p<0.05).
