Fig. 4. Assessment of BAK-mediated necrosis during MI/R.
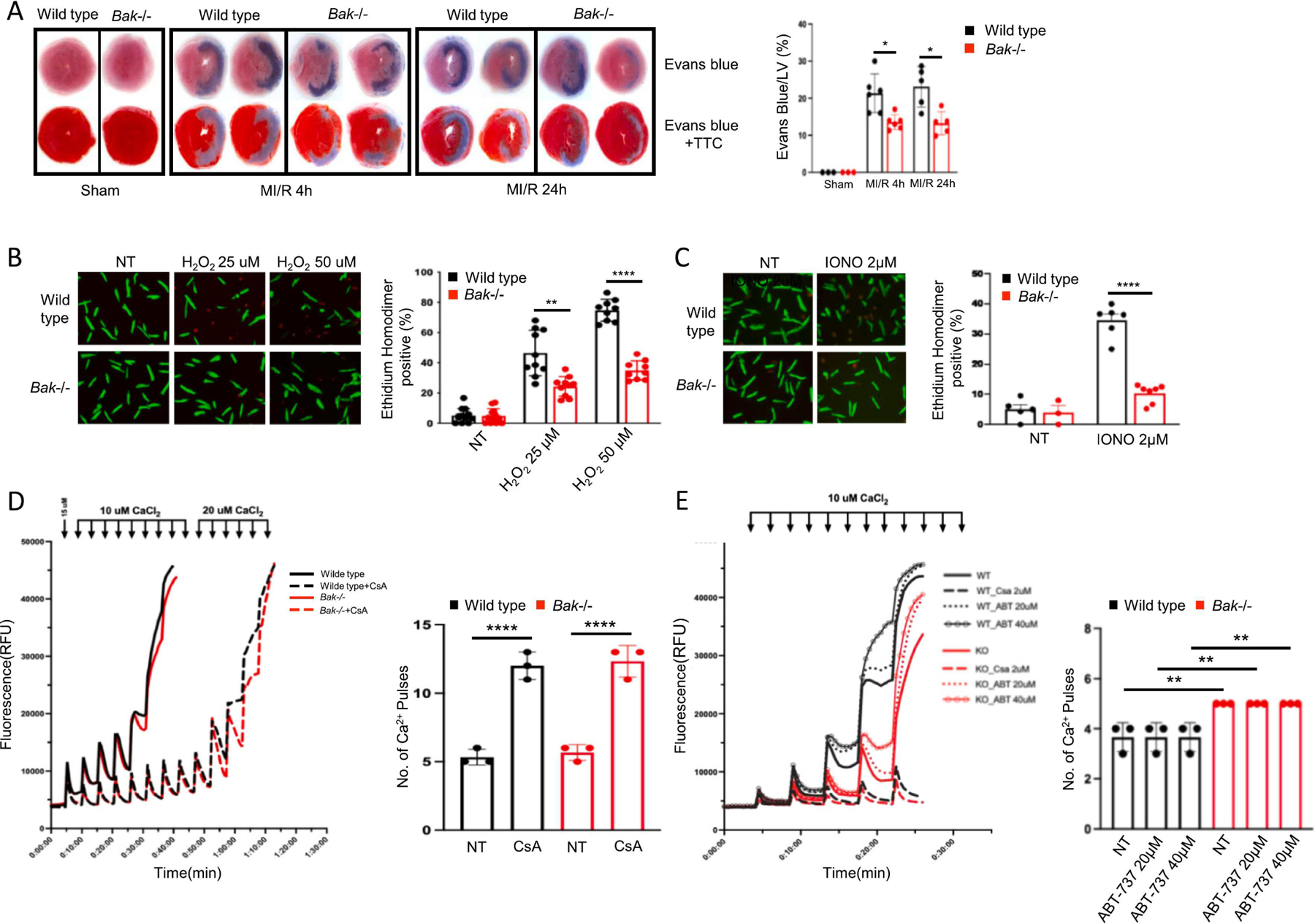
B. Representative images and quantification of necrosis assessed by staining with Evans blue dye administered pre-mortem at the time of reperfusion by itself (top) or combined with post-mortem TTC staining (bottom) in hearts of wild type (black) and Bak−/− (red) mice subjected to sham operation (harvested 24 h later) or 45 min ischemia and 4 h or 24 h reperfusion (N= 3 sham per genotype, 6 MI/R 4 h per genotype, 5 MI/R 24 h per genotype male mice). B. Isolated adult mouse cardiomyocytes from wild type (black) and Bak−/− (red) mice treated with the indicated concentrations of H2O2 and cell death scored 30 min later by ethidium homodimer staining of nucleus. C. Isolated adult mouse cardiomyocytes from wild type (black) and Bak−/− (red) mice treated with the indicated concentration of ionomycin and cell death scored 30 min later with ethidium homodimer. For B. and C, N = 3 independent experiments, each in duplicate with 2–3 fields scored per replicate. D, E. Two independent calcium retention assay experiments using cardiac mitochondria isolated from wild type or Bak−/− mice (N=3 mice of each genotype in each experiment). CsA and ABT-737 denote pretreatment of mitochondria with cyclosporine A (2 μ) or ABT-737 (at the indicated concentration) for 20 min. Data – mean ± SEM. Statistic: ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, **** P < 0.0001.
