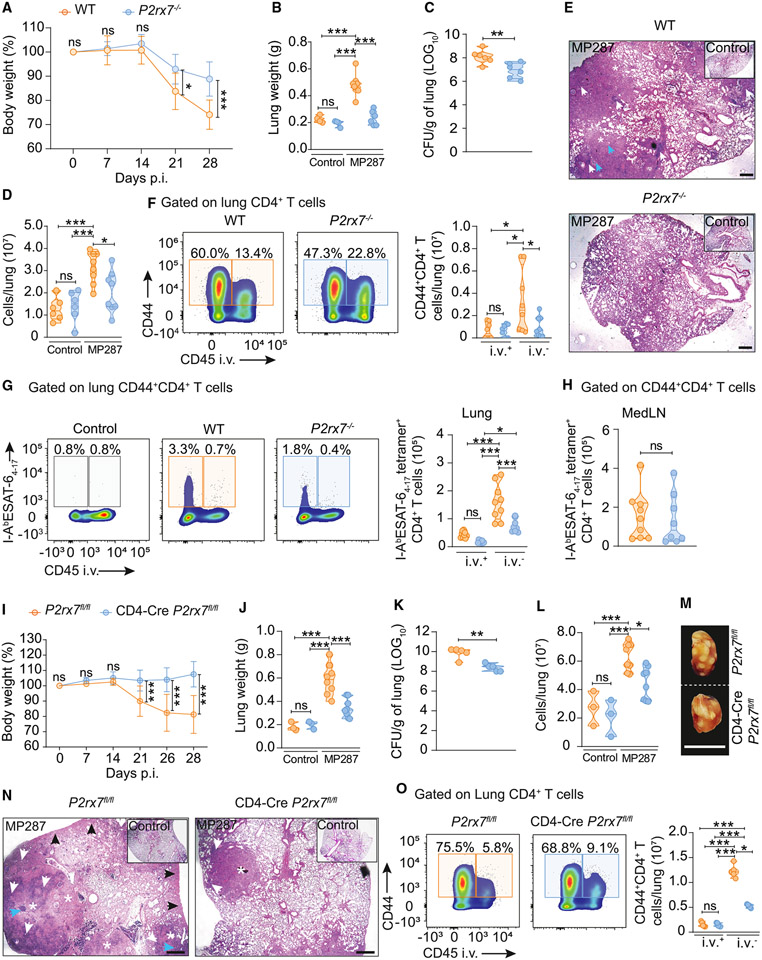
Figure 2. T cell-specific P2RX7 promotes lung parenchymal CD4+ T cell accumulation and severe TB caused by hypervirulent mycobacteria.
WT (C57BL/6 or P2rx7fl/fl), P2RX7-KO (P2rx7−/−), or T cell-P2RX7-KO (CD4-Cre P2rx7fl/fl) mice were infected with ~100 CFU of Mbv MP287. Non-infected mice were used as controls.
(A and I) Percentages of body weights in relation to day 0 of WT, P2RX7-KO, or T cell-P2RX7-KO mice.
(B and J) Lung weight values of WT, P2RX7-KO, or T cell-P2RX7-KO mice.
(C and K) CFU numbers per lung of WT, P2RX7-KO, or T cell-P2RX7-KO mice.
(D and L) Total lung cell numbers of WT, P2RX7-KO, or T cell-P2RX7-KO mice.
(E) Representative lung sections stained with H&E of WT or P2RX7-KO mice. Scale bars, 500 μm.
(F) Left: flow-cytometry plots of CD44 and CD45i.v. in lung CD4+ T cells. Right: average numbers of CD45i.v.+ and CD45i.v.− CD44+CD4+ T cells/lung.
(G) Left: flow-cytometry plots of I-AbESAT-64-17 and CD45i.v. expression in lung CD4+ T cells. Right: average numbers of CD45i.v.+ and CD45i.v.− I-AbESAT-64-17+CD44+CD4+ T cells/lung.
(H) Average numbers of medLN I-AbESAT-64-17+CXCR3+CD4+ T cells.
(M) Macroscopic images of right upper lung lobes of WT and T cell-P2RX7-KO mice. Scale bars, 1 cm.
(N) Representative lung sections stained with H&E of WT and T cell-P2RX7-KO mice. Scale bars, 500 μm.
(O) Left: flow-cytometry plots of CD44 and CD45i.v. in lung CD4+ T cells of WT and T cell-P2RX7-KO mice. Right: average numbers of CD45i.v.+ and CD45i.v.− CD44+CD4+T cells/lung.
Data from three independent experiments: n = 3–5/experimental group per experiment. Data shown as means ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA (Tukey post tests) (B, D, F, G, J, L, and O) or unpaired t tests (A, C, H, I, and K).