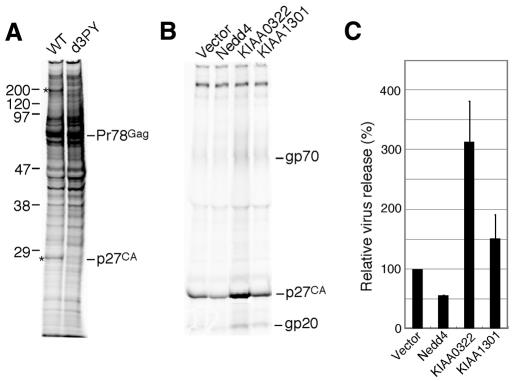
Fig. 1. Identification of the cellular factors involved in M-PMV budding. (A) Proteins that interact with the PPPY sequence within the L domain of M-PMV. COS-7 cells were transfected with either pSHRM15 (WT) or pd3PY and labelled for 6 h at 48 h after transfection. The cells were lysed with TNE buffer, and then the lysate was subjected to immunoprecipitation with rabbit anti-Pr78gag antiserum. The proteins coimmunoprecipitated with Gag were resolved by SDS–PAGE. Asterisks on the left indicate differences between wild-type and d3PY. The apparent molecular masses of these components are shown on the left (in kDa). (B) Effects of the expression of Nedd4, KIAA0322 (BUL1) or KIAA1301 on virus production. COS-7 cells were cotransfected with pSHRM15 and expression plasmids for Nedd4, KIAA0322 or KIAA1301. Extracellular virions were pelleted from the culture fluids of the labelled cells and then subjected to immunoprecipitation with rabbit anti-M-PMV antiserum. The migration positions of viral proteins are indicated on the right. These results were representative of three independent experiments. (C) Intensity of the band for viral capsid protein p27 in (B) was quantitated as described in Methods. The extent of p27 released from wild-type proviral vector-transfected cells was set to 100%. The data represent averages and SDs of three independent experiments.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.