Extended Data Figure 6: Stathmin-2 related genes remain unchanged upon stathmin-2 loss.
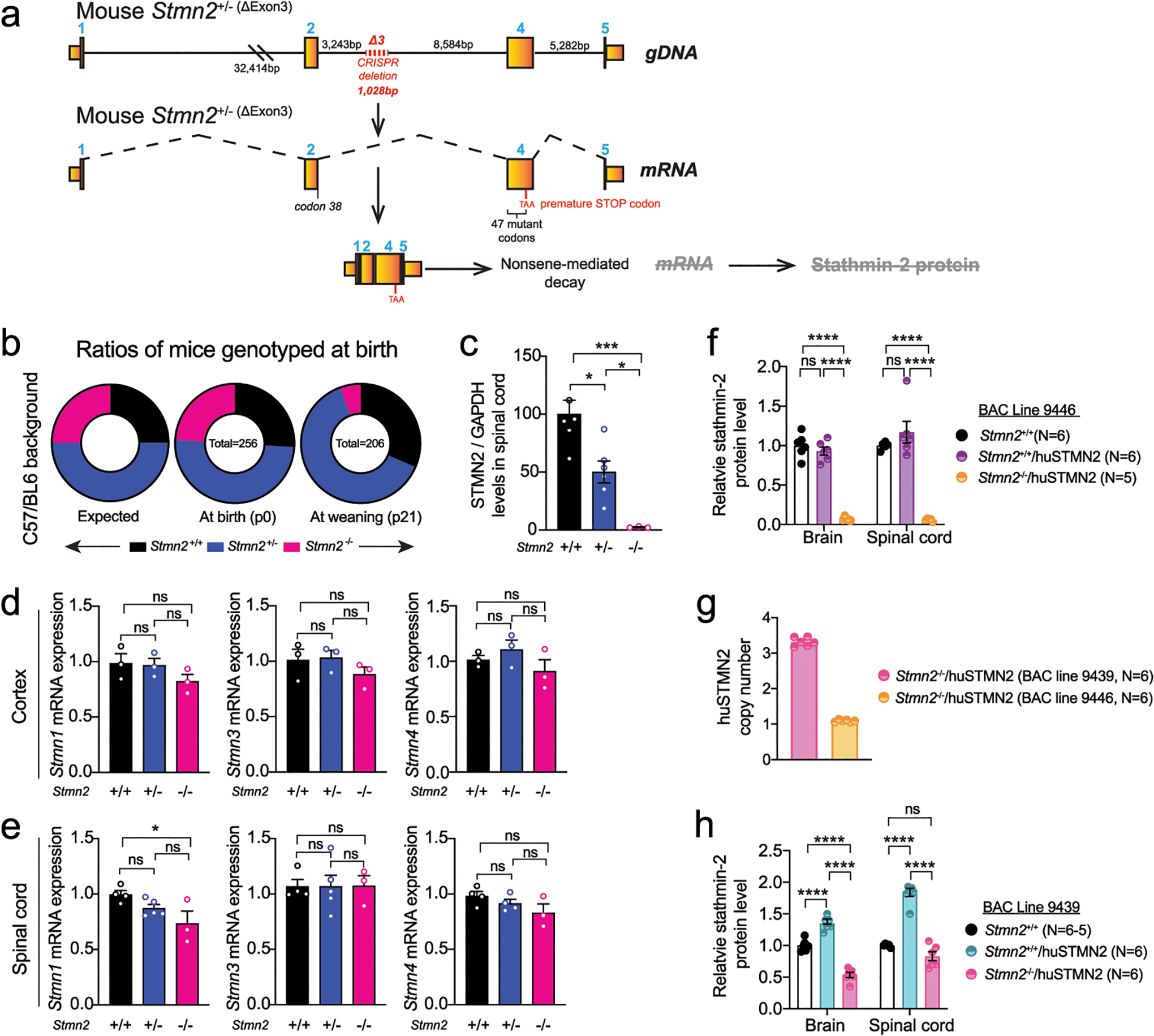
(a) Diagram of genome editing design by CRISPR-Cas9-mediated excision of mouse Stmn2 exon 3 that leads to complete absence of stathmin-2 protein. (b) Ratios of mice expected, genotyped at birth (p0) and alive at weaning age (p21) from Stmn2+/− to Stmn2+/− crossing in C57/BL6J background. (c) Stathmin-2 protein quantification from the immunoblots in Fig. 5d normalized by GAPDH level. N=6 animals per Stmn2+/+ and Stmn2+/−; n=3 animals per Stmn2−/−. Statistical analysis by two-sided, one-way ANOVA post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison test. * P = 0.0103; * P = 0.041; *** P = 0.0003. (d,e) Measurement of mouse Stmn-1, −3 and −4 mRNA levels extracted from 12-month-old cortex (d) and spinal cord (e) of Stmn2+/+, Stmn2+/− Stmn2−/− mice. Gapdh was used as an endogenous control gene. N=3 animals per genotype (d), and n= 3–5 per genotype (e). Statistical analysis by two-sided one-way ANOVA post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (f) Stathmin-2 protein quantification from brain and spinal cord extract of Stmn2+/+, Stmn2+/+/huSTMN2 and Stmn2−/−/huSTMN2 (BAC line 9439) by immunoblotting. N=5 animals per genotype. (g) huSTMN2 transgene copy numbers measured in BAC transgenic lines 9439 and 9446. N=6 animals per genotype. (h) Stathmin-2 protein quantification from brain and spinal cord extract of Stmn2+/+, Stmn2+/+/huSTMN2 and in Stmn2−/−/huSTMN2 (BAC line 9446) by immunoblotting. N=6 animals per genotype. (f,h) Statistical analysis by two-sided, two-way ANOVA post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, (P <0.0001). All panels: Each data point represents an individual mouse. Bar graphs represent mean values. Error bars plotted as SEM. ****, P <0.0001; ***, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.01; *, P <0.05; ns, P >0.05.
