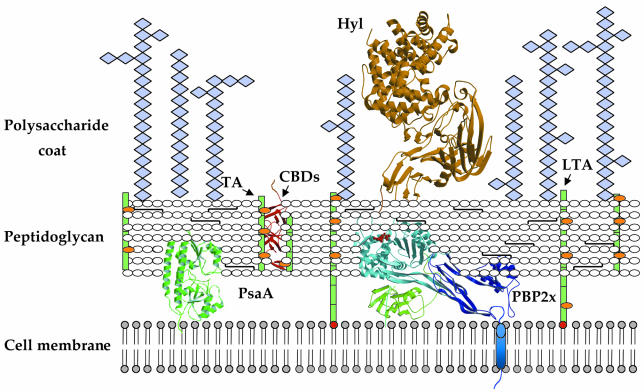
Fig. 2. Schematic representation of the streptococcal cell wall. Teichoic acids (TAs) and lipoteichoic acids (LTAs) (both in green) are carbohydrate phosphate polymers rich in choline (orange spheres). TAs are linked to the peptidoglycan via a phosphodiester linkage, whereas LTAs are linked to the cell membrane via a C-terminal fatty acyl group (in red). Choline-binding proteins are linked to cell-wall TAs or LTAs via choline-binding domains (CBDs) (red ribbon diagram). Pneumococcal surface antigen (PsaA) is located underneath the peptidoglycan layer and is attached to the cell membrane via an LXXC motif; penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) are located in the periplasmic space and interact with the peptidoglycan, and display a single, N-terminal transmembrane helix (in blue). Hyaluronate lyase (Hyl) is tethered to the peptidoglycan via an LPXTG motif.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.